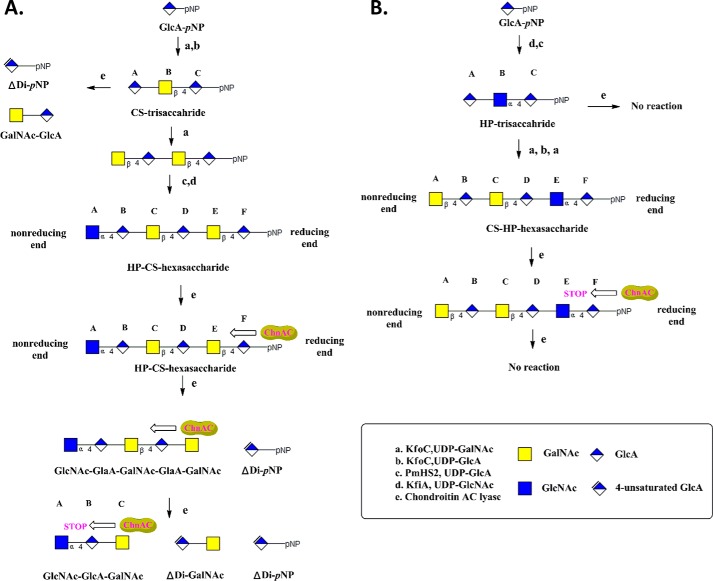
FIGURE 1.
Scheme for the synthesis of homogenous oligosaccharides and the schematic representation of AsChnAc cleavage of these substrates. The synthesis was initiated from GlcUA-pNP using a chemoenzymatic approach. The starting monosaccharide was elongated to the desired size using glycosyltransferases according to the methods described in “Experimental Procedures.” Four oligosaccharides were synthesized in this way, and their purities were assessed by (PAMN)-HPLC (Figs. 2, A, D; 3A; and 4A). The structures of these oligosaccharides were evaluated by ESI-MS analysis (Figs. 2, B and E; 3B; and 4B). KfiA is an N-acetyl glucosaminyl transferase from E. coli strain K5. pmHS2 was obtained from P. multocida heparosan synthase. KfoC is a chondroitin polymerase from E. coli K4. A, scheme for the synthesis of the CS-trisaccharide and HP-CS-hexasaccharide, and the cleavage of these oligosaccharide substrates by AsChnAC. The degradation products resulting from the treatment of CS-trisaccharide with AsChnAC were determined by (PAMN)-HPLC and ESI-MS analyses, which revealed the presence of two new compounds (GalNAc-GlcA and ΔDi-pNP). When the β-1,4 linkages between the N-acetylhexosamine and GlcA residues (i.e. residues Cys and Asp or residues Glu and Phe) were present at the reducing end of the HP-CS-hexasaccharide, AsChnAC displayed a consecutive cleavage pattern. The products of this degradation process were determined to contain GlcNAc-GlcA-GalNAc, ΔDi-GalNAc, and ΔDi-pNP by ESI-MS analysis. The pentasaccharide GlcNAc-GlaA-GalNAc-GlaA-GalNAc was identified following the partial digestion of the HP-CS-hexasaccharide. B, scheme for the synthesis of the HP-trisaccharide and CS-HP-hexasaccharide, and the cleavage of these oligosaccharide substrates by AsChnAC. When there was one α-1,4 linkage between the N-acetylhexosamine and GlcA residues at the non-reducing end of the substrate, as in the HP-trisaccharide and the CS-HP-hexasaccharide, ChnAC did not exhibit any cleavage activity. By setting the ChnAC-uncleavable site on the reducing or non-reducing terminus, we have shown that ChnAC cleaves oligosaccharide chains from the reducing end toward the non-reducing end.