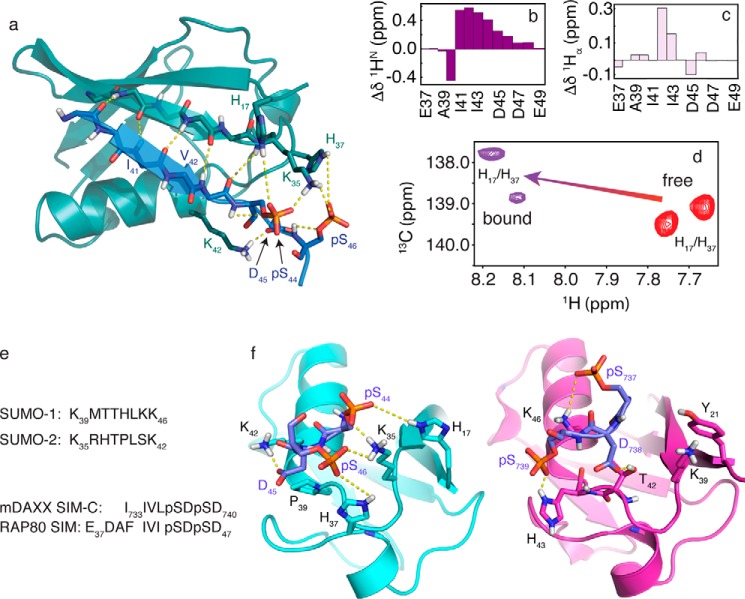
FIGURE 6.
a, NMR structure for the SUMO-2·pRAP80-(37–49) complex. The main chain atoms are shown in the schematic representation (RAP80 SIM, blue; SUMO-2, teal). Key electrostatic interactions are indicated by yellow dashed lines, and include hydrogen bonds between the main chain atoms of the SIM hydrophobic module, and interactions between the SUMO-2 specificity module and the negatively charged side chains of the SIM. b, 1HN main chain amide chemical shift changes (bound-free) for pRAP80-(37–49) upon binding of SUMO-2. c, 1Hα main chain chemical shift changes (bound-free) for pRAP80-(37–49) upon binding of SUMO-2. d, two-dimensional 1H-13C HSQC NMR spectra showing side chain chemical shifts for the SUMO-2 Hδ2 atoms from residues His17 and His37 in the free state (red) and upon interaction with pRAP80-(37–49) (purple). e, sequence alignment for the SIM binding loop from SUMO-1 and -2, and the alignment for the SIM from RAP80 and that from “modified” DAXX, which contains residues from the PML SIM N-terminal to Ile733 to facilitate crystallization. f, comparison of the structure of the SUMO-2·pRAP80-(37–49) complex with the SUMO-1·pDAXX-(733–740) complex (PDB code 4WJP). SUMO-1 and -2 are shown in purple and cyan, respectively, the electrostatic SUMO recognition modules from the pSIMs are shown in blue. Dashed yellow lines highlight key intermolecular electrostatic interactions. The hydrophobic SUMO recognition modules from the pSIMs are not shown for clarity.