FIGURE 5.
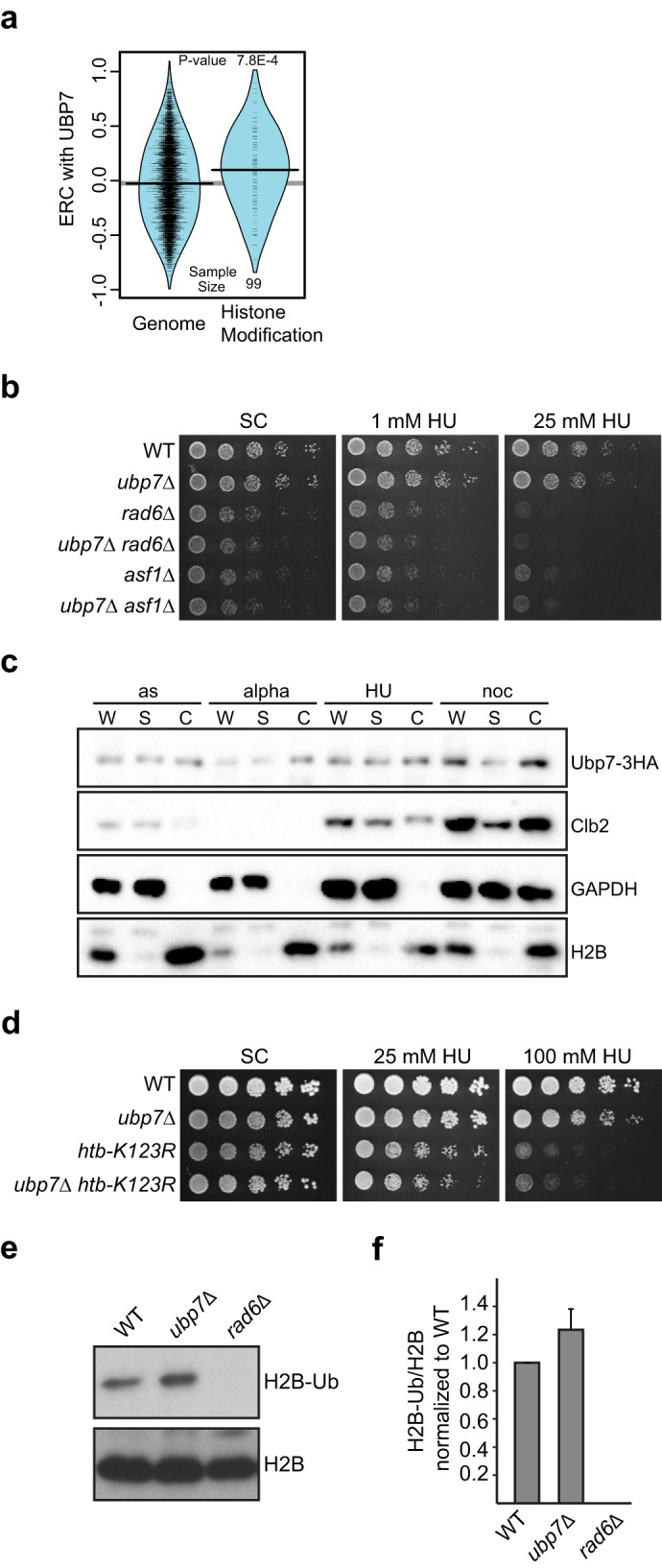
Deletion of UBP7 affects H2B ubiquitination. a, ERC values between Ubp7 and histone modification genes are elevated significantly compared with the genome-wide distribution. The violin plot shows the actual ERC values (tick marks) and their smoothed densities. b, genetic interaction of ubp7Δ with the histone chaperone ASF1 and histone-modifying E2 RAD6. Shown are 5-fold serial dilutions of the indicated strains on plates containing 1 and 25 mm HU, respectively. c, chromatin-binding assay for Ubp7–3HA. Shown are Western blotting analyses of whole-cell extract (W), supernatant (S), and chromatin-bound (C) fractions from asynchronous cultures (as) or those synchronized in G1 (alpha), S (HU), and G2/M phase (noc). Antibodies against HA, Clb2, GAPDH, and H2B were used. d, genetic interaction of ubp7Δ with htb-K123R. Shown are 5-fold serial dilutions of the indicated strains on plates containing the respective amounts of HU. Note that the strains used in this figure were in the FY2 genetic background, and, therefore, we observed a modest variation in the DNA damage sensitivity of ubp7Δ cells. e, steady-state H2B ubiquitination at Lys-123 in untreated asynchronous wild-type and ubp7Δ cultures. Shown is a Western blotting analysis for ubiquitinated H2B and total H2B. f, quantification of e by determining the ratio of H2B-Ub to total H2B and normalizing to the wild type. The graph represents the mean of four independent trials ± S.D.
