FIGURE 1.
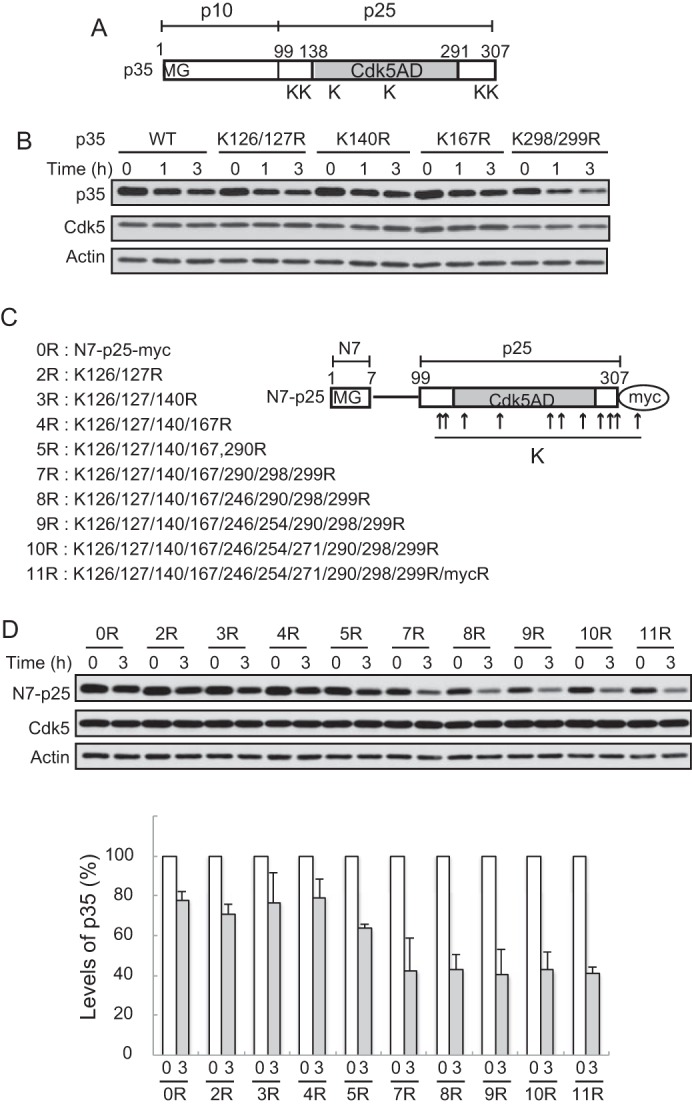
Effect of Lys-to-Arg mutations in the C-terminal p25 region of p35 on degradation. A, schematic representation of the p35 molecule. p35 consists of the N-terminal p10 and the C-terminal p25 Cdk5 activation domain (Cdk5AD). Lysine residues that we thought possible ubiquitination sites are indicated by K. B, effect of Arg mutations at these possible ubiquitination sites on the degradation of p35. Neuro2a cells expressing p35 (WT) or its Arg mutants K126R/K127R, K140R, K167R, or K298R/K299R were treated with CHX for 1 or 3 h. The amounts of p35 protein were assessed by immunoblotting with anti-p35 (top). Cdk5 is shown in the middle. Actin is the loading control. C, N7-p25 molecule and its Arg mutants at Lys residues. N7-p25 is p25 fused with the seven N-terminal amino acids (N7), where there is a myristoylation consensus motif. The positions of the Lys residues are indicated by arrows. The sequential mutation of all of the Lys to Arg in p25 is shown on the left. 11R contains an Arg mutation at the Lys in the myc-tag sequence. D, degradation of Arg mutants of N7-p25 in Neuro2a cells. N7-p25 and its Arg mutants coexpressed with Cdk5 into Neuro2a cells were detected by Immunoblotting with anti-myc after treatment with CHX. Quantification is shown in the lower panel (mean ± S.E., n = 3).
