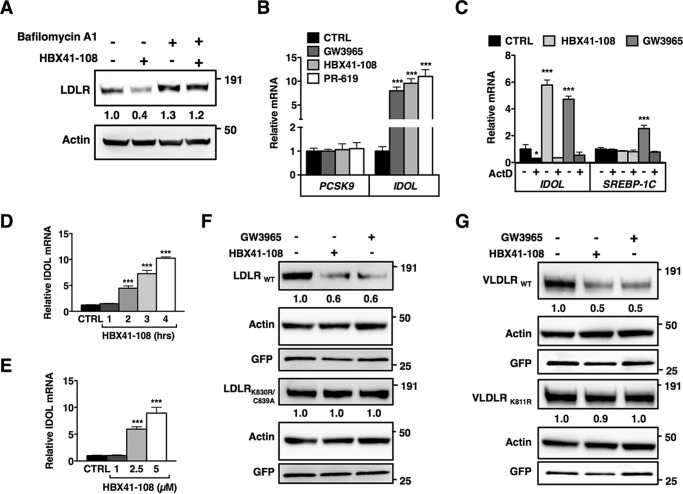
FIGURE 3.
DUB inhibition promotes ubiquitylation-dependent lysosomal degradation of the LDLR. A, HepG2 cells were pretreated for 4 h with vehicle or bafilomycin A1 (100 nm) and subsequently treated for an additional 2 h treatment with 5 μm HBX41-108. Total cell lysates were immunoblotted as indicated. Immunoblots were quantified, and the mean intensity of the LDLR normalized to β-actin relative to control treated cells is indicated (n = 4). B, HepG2 cells were treated with 1 μm GW3965 (6 h), 5 μm HBX41-108, or 50 μm PR-619 (2 h). Subsequently, mRNA expression of PCSK9 and IDOL were determined by qPCR. Each bar represents the mean ± S.D. relative to vehicle-treated control cells (n = 3). C, HepG2 cells were treated with 2 μm actinomycin D (2 h) and then treated with 1 μm GW3965 or 5 μm HBX41-108 for 4 h. Expression of IDOL and SREBP-1c was determined by qPCR. Each bar represents the mean ± S.D. relative to vehicle-treated control cells (n = 3). D and E, HepG2 cells were treated with 5 μm HBX41-108 for the indicated time (D) or for 2 h (E) with the indicated concentration of HBX41-108 and mRNA expression of IDOL was determined by qPCR (n = 4). F and G, HeLa cells were co-transfected with expression plasmids for LDLRWT, VLDLRWT, the ubiquitylation mutants LDLRK830R,C839A and VLDLRK811R, and GFP (to monitor transfection efficiency). The cells were subsequently treated for 24 h with 1 μm GW3965 or for 4 h with 5 μm HBX41-108. The total cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting as indicated. Immunoblots are representative of at least three independent experiments. Images were quantified and intensity of the LDLR and VLDLR was normalized and displayed as mean relative to vehicle-treated control cells (n = 3). *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001. CTRL, control.