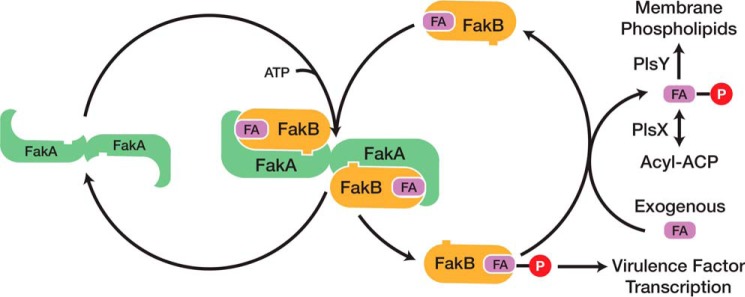
FIGURE 1.
Catalytic cycle of Fak and its role in phospholipid synthesis and virulence factor transcription. Fak consists of a dimeric ATP-binding protein (FakA) and a fatty acid-binding protein (FakB). The first step in the reaction is the binding of FakB to FakA. The fatty acid bound to FakB is then phosphorylated by FakA, and the acyl-PO4-bound FakB is released from the complex. Phosphorylated FakB participates in the activation of virulence factor transcription by an unknown biochemical cascade. In the presence of an exchangeable fatty acid pool in the cell membrane, the acyl-PO4 bound to FakB exchanges with a fatty acid to regenerate the substrate for FakA. The released acyl-PO4 is either used by PlsY to initiate phospholipid synthesis or converted to acyl-acyl carrier protein by PlsX where it can be used by the PlsC acyltransferase or enter the fatty acid elongation cycle.