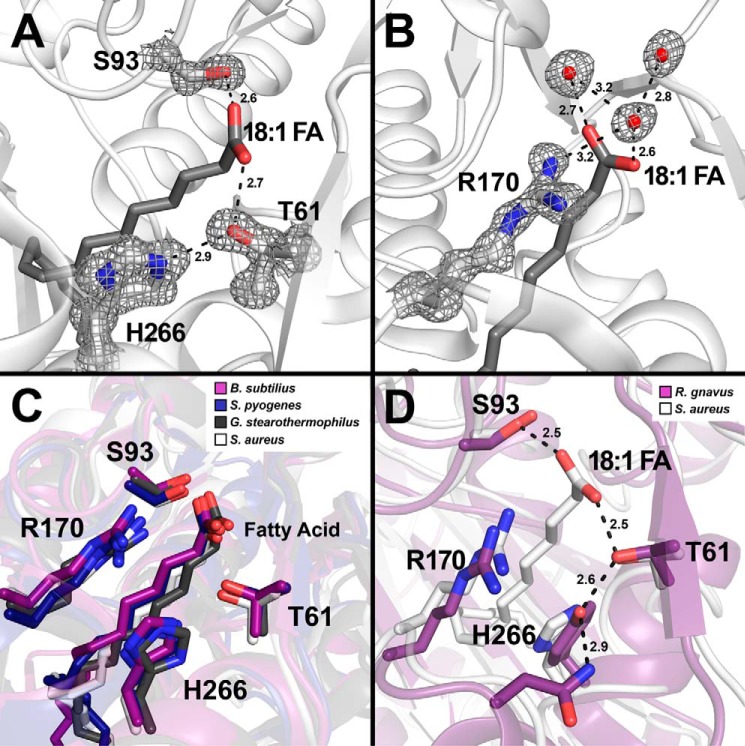
FIGURE 3.
Close-up view of the hydrogen bond network that anchors the fatty acid in FakB2. S. aureus FakB2 crystal structure models are shown in white schematic representation with oleate presented as sticks (dark gray). Selected residues are shown as sticks with oxygen and nitrogen atoms in red and blue, respectively. Waters are depicted as red spheres and hydrogen bonds as black dashed lines along with their distances in Å. A and B, representative simulated annealing 2mFo − DFc composite omit map density (dark gray) contoured at 1.5 σ is rendered around key residues and waters. A, omit map of the fatty acid carboxyl binding pocket highlighting the FakB2 residues Thr-61, Ser-93, and His-266 involved in the hydrogen bond network that fixes the fatty acid carboxyl group. B, omit map illustrating Arg-170 and its interactions with three structured water molecules positioned next to the fatty acid carboxyl group. C, close-up view of the fatty acid binding pocket of FakB2 with the side chains of residues Thr-61, Ser-93, Arg-170, and His-266 superimposed over the FakB2 structures from B. subtilis (PDB code 3FYS; purple), S. pyogenes (PDB code 2G7Z; dark blue), and G. stearothermophilus (PDB code 1PZX; black). D, close-up view of the fatty acid binding pocket of FakB2 with selected residues Thr-61, Ser-93, Arg-170, and His-266 superimposed over the homologous structure from R. gnavus (PDB code 3JR7; purple), which has a tyrosine substituted for histidine in the hydrogen bond network.