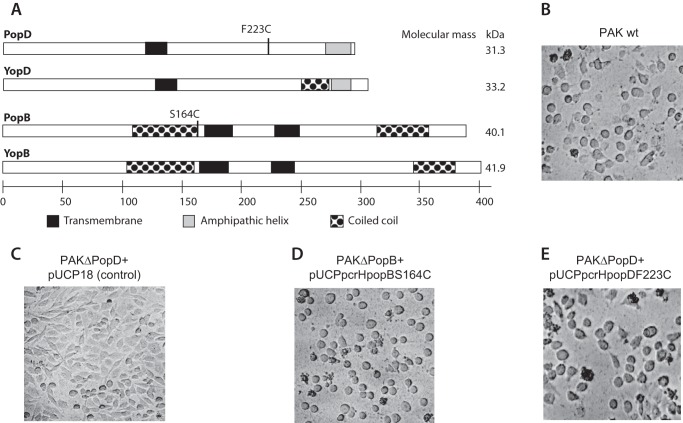
FIGURE 1.
PopBS164C and PopDF223C derivatives were active for effector translocation. A, scheme of the primary structure of P. aeruoginosa PAO1 translocators PopD (gi 9947683) and PopB (gi 9947682) compared with the homologue Y. enterolcolitica translocators YopD (gi 586795) and YopB (gi 122815801). Location of the single Cys modifications introduced for probe labeling is indicated on PopD and PopB. Predicted hydrophobic segments, amphipathic helices, and coiled coils are shown. The molecular mass for each translocator is shown on the right. The scale at the bottom indicates amino acid number. The activity of the PopB (or PopD) derivative was indistinguishable from the wild-type protein when evaluated for their ability to complement a popB deletion strain (or a popD deletion strain). The activity of the translocators was assessed by the characteristic rounding up of the infected target cells due to actin cytoskeleton disruption caused by effector translocation (15). Strains used in this assay were P. aeruginosa PAK WT (B), PAKΔpopD complemented with pUCP18 (C), PAKΔpopB complemented with pUCPHBS164C (D), and PAKΔpopD complemented with pUCPHDF223C (E). The PAKΔpopB control showed no effect on cell morphology as shown for the PAKΔpopD control in panel C (not shown).