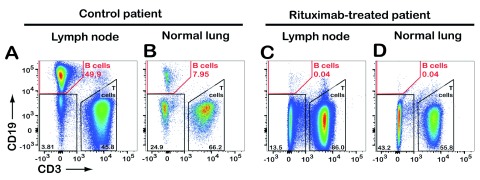
Figure 2. Rituximab depletes B cells in lung-associated lymph node and normal lung tissue.
Upon chest surgery for removal of tumor-containing lung lobe from a patient previously treated with rituximab, a lung-associated lymph node and normal lung tissue samples were analyzed by flow cytometry. Results from a control lung cancer patient (not treated with rituximab) are shown for comparison. Both patients were diagnosed with lung adenocarcinoma. Live leukocytes (CD45-positive, propidium iodide-negative) were gated and analyzed further for expression of CD19 (B cells) and CD3 (T cells). Numbers indicate the percentage of cells detected in each gate.