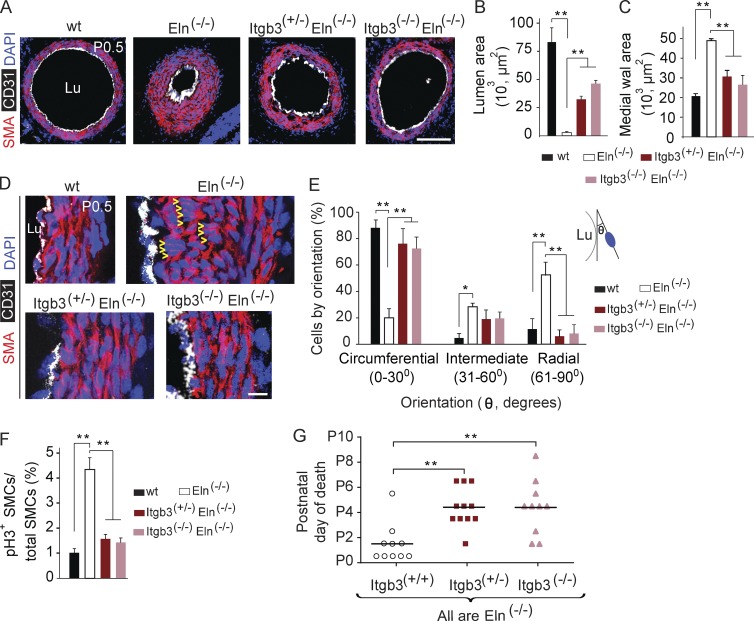
Figure 6.
Reduced integrin β3 gene dosage inhibits aortic hypermuscularization and extends viability of elastin nulls. (A) Transverse descending aortic sections of newborns of indicated genotype at P0.5 were stained for SMA, CD31, and nuclei (DAPI). (B and C) Aortic lumen and medial wall area were determined from sections as shown in A; n = 3 aortas per genotype, 3 sections per aorta. Note that reduced Itgb3 dosage attenuates Eln(−/−) aortic hypermuscularization. (D) Sections cut and stained as in A with high power magnification of the aortic wall demonstrating that wild-type SMCs are circumferentially oriented, whereas the abnormal radial orientation of SMCs in the inner layers of the Eln(−/−) aorta is prevented by reducing Itgb3 dosage. Arrowheads indicate examples of radially oriented SMCs in Eln(−/−) aorta. (E) Quantification of nuclear orientation of cells in inner three aortic smooth muscle layers of embryos of the indicated genotype at P0.5 with respect to the tangent of the lumen boundary; n = 3 aortas, and >200 SMCs were scored for each genotype. (F) Proliferative index (fraction of pH3+ cells) of aortic SMCs of embryos of the indicated genotype at E17.5. 20 sections per embryo were analyzed, and the number of embryos analyzed and pH3+ aortic SMCs detected were 3 embryos and 172 SMCs for wild type, 3 and 787 for Eln(−/−), 2 and 184 for Itgb3(+/−)Eln(−/−), and 2 and 163 for Itgb3(−/−)Eln(−/−). (G) The age of death of each Eln(−/−) newborn is classified by Itgb3 genotype, with bars indicating the mean age of death. Reduced Itgb3 gene dosage increases viability of elastin-null pups. Data are presented as mean ± SD. ANOVA was used. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. Lu, aortic lumen. Bars: (A) 100 µm; (D) 10 µm.