Fig. 4.
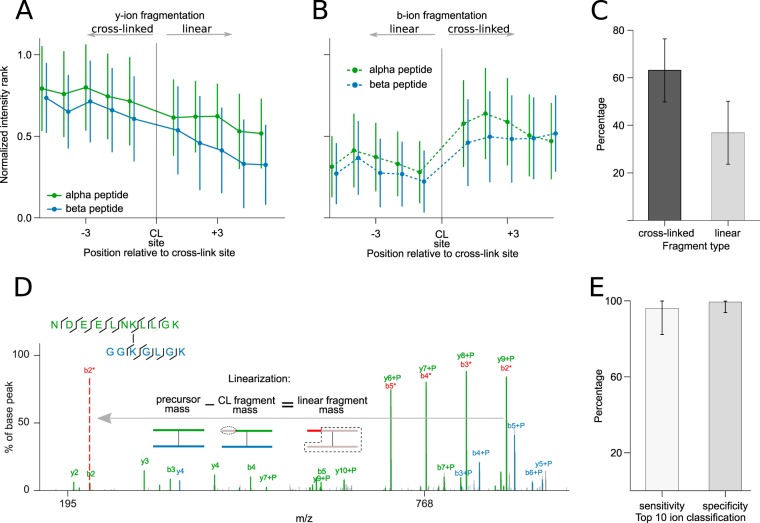
Cross-linked peptide fragmentation patterns. Influence of the cross-link site (CL site) on y-ion (A) and b-ion yield (B), respectively. Longer y-ions are located to the left of the cross-link site; longer b-ions are located to the right of the cross-link site. Fragment intensities were transformed to ranks, with high intensities having a higher rank, and then normalized by the number of fragments in a spectrum. Error bars correspond to the standard deviation of all measured intensities at a relative position. (C) Distribution of cross-linker containing and linear fragments in cross-linked peptide spectra, respectively. (D) Example spectrum reflecting preferred cleavage of cross-linked fragments and an exemplary linearization of the cross-linked y7-ion of the alpha peptide. As shown in the pictogram of the linearization process, the y9-ion is transformed to the b2 ion (which was also observed as low intense peak) by subtracting the fragment mass from the precursor mass. Similarly, the y8 ion can be transformed to the b3 ion, which is indicated by the annotation with a '*' in the spectrum. (E) Sensitivity and specificity of correctly assigned cross-linked and linear fragments by their charge and mass from the top ten identified ions. The underlying data were extracted from 910 PSMs at a 5% FDR. For bar plots, the height and error bars refer to the mean and the standard deviation of all evaluated PSMs. The linear alpha peptides are also shown in Supplemental Fig. S7.