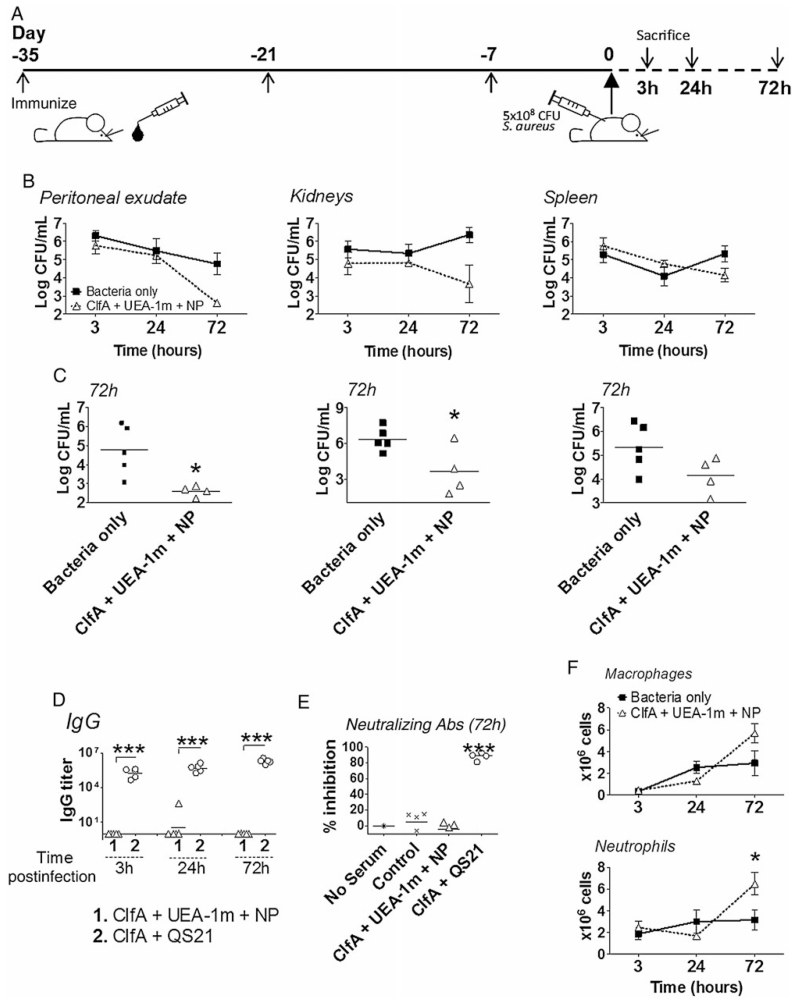
Figure 2.
The induction of cellular immunity by a nasal targeted nanoparticulate Staphylococcus aureus vaccine is sufficient for clearance of a systemic S. aureus infection. A, Immunization strategy. Mice were immunized intranasally on days 1, 14, and 28 with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) or with clumping factor A (ClfA; 2 μg) and Ulex europaeus agglutinin I peptidomimetic (UEA-1m; 10 μg) attached to nanoparticles (NP). Mice were sacrificed at time 0 (day 35, before infection), and at 3, 24, and 72 hours after intraperitoneal infection with 5 × 108 colony-forming units (CFU) S. aureus (strain PS80). Data are representative of 2 independent experiments. B and C, Bacterial counts. The peritoneal exudate, kidneys, and spleen were harvested at each time point, homogenized, and cultured, and CFUs were determined. CFU burden is expressed as the mean ± SEM over time (n = 5, top panel), and in each tissue at 72 hours postinfection. C, Statistical significance between groups is denoted by *P < .05 and **P < .01 (1-tailed unpaired Student t test). D and E, Antibody responses following challenge. Anti-ClfA immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibody titers were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay on serum samples recovered at each timepoint postinfection. The presence of neutralizing antibodies was determined by measuring the ability of serum to inhibit ClfA-mediated S. aureus adherence to fibrinogen. Staphylococcus aureus was preincubated with serum, and adherence to fibrinogen was calculated as a percentage of values measured in control wells lacking serum. Each data point represents an individual animal (n = 5); the black bars denote the mean. ***P < .001 by 1-way analysis of variance and Tukey posttest. F, Phagocytes at the site of infection. The total numbers of peritoneal macrophages and neutrophils in control and vaccinated mice were determined by flow cytometry at 3, 24, and 72 hours following infection. *P < .05 by 1-tailed unpaired Student t test (n = 5).