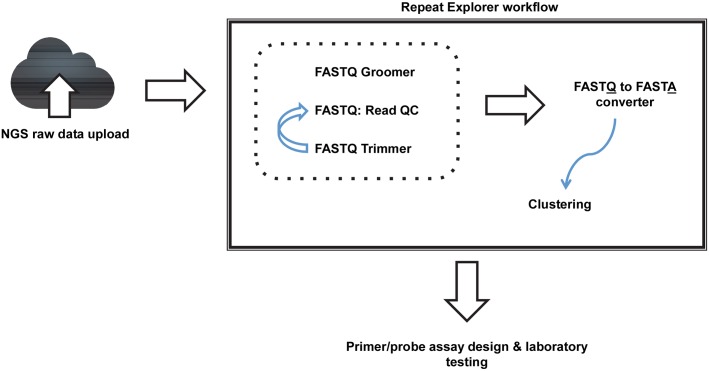
Fig 1. Workflow for repeat analysis.
Output data from a next-generation sequencing run are uploaded to the RepeatExplorer Galaxy-based platform. During the QC and manipulation phase, the FASTQ Groomer tool is used to convert sequence reads into Sanger format. The FASTQ: READ QC tool is then used to verify the quality of the reads before removing unnecessary sequence (i.e. adapter sequences, etc.) from the ends of each read using the FASTQ Trimmer tool. The QC analysis is then repeated, and the FASTQ to FASTA converter tool is used to convert each read into FASTA format. Using these DNA sequence reads as input, sequences undergo clustering, during which an “all-to-all” sequence comparison is performed, and similar sequences are grouped together into clusters. Clusters containing the most highly repetitive sequences are then selected as putative diagnostic targets to be used for primer and probe-based real-time PCR assay design.