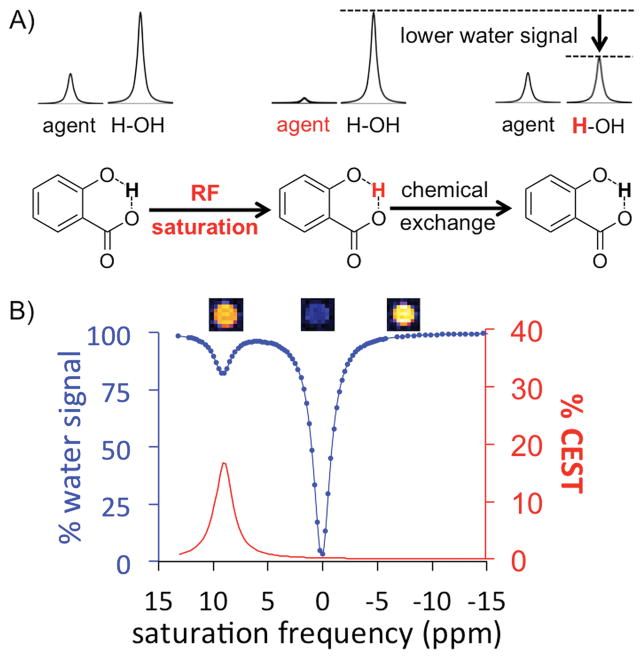
Figure 1.
Mechanism of CEST MRI. A) Radio frequency saturation of the proton “trapped” between the two oxygens of salicylic acid results in the loss of the MRI signal from this proton. After exchanging this saturated proton with a proton on water, some of the MRI signal of water is lost, which can be measured with MRI.5 B) A CEST spectrum of 25 mM salicylic acid shows a CEST signal at 9.25 ppm. MR images of the sample are shown above the CEST spectrum, showing the decreased MR signal with selective saturation applied at 9.25 ppm relative to −9.25 ppm as a reference, and almost no MRI signal with selective saturation applied at 0 ppm. The CEST spectrum was obtained with a 5 s, 5 μT saturation pulse using a 7T MRI instrument at 37 °C.