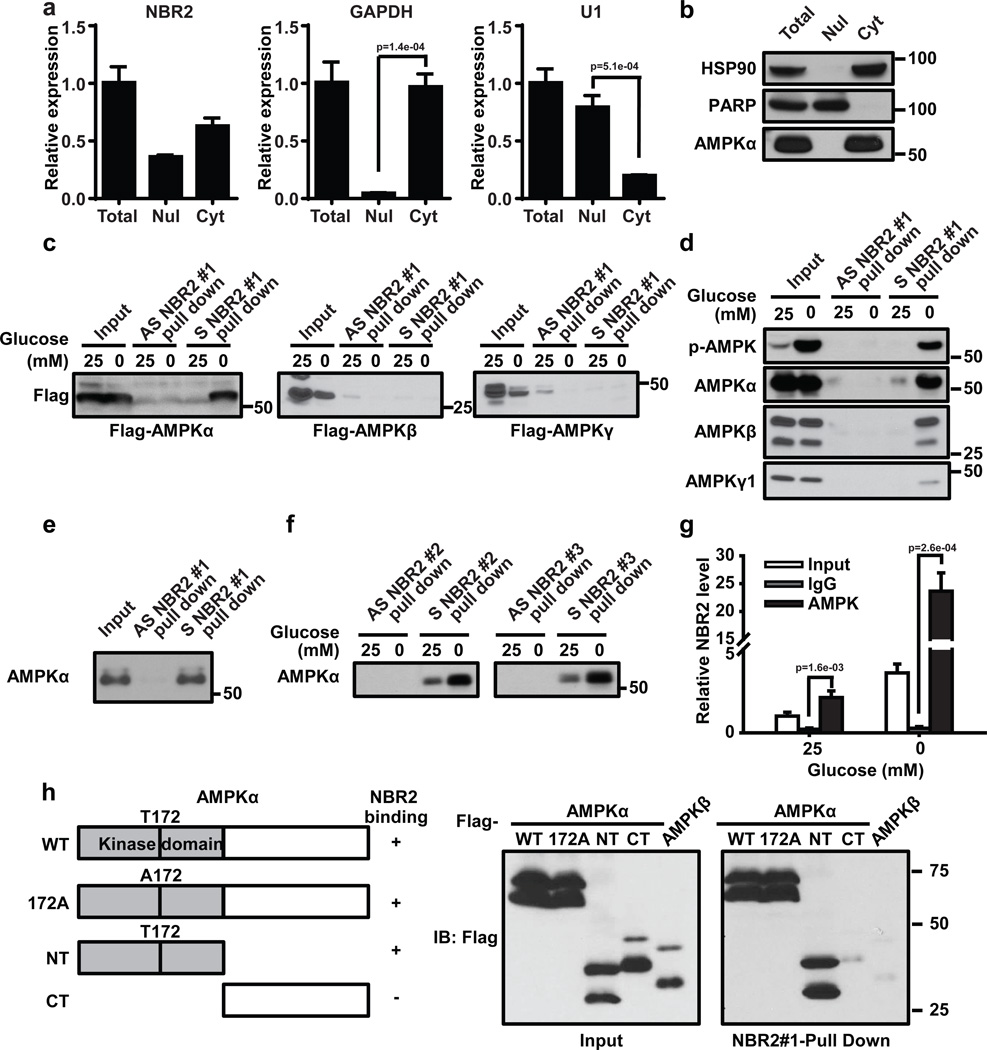
Figure 5. Energy stress induces NBR2 interaction with AMPK.
(a, b) Nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions of 786O cells were subjected to either real-time PCR (a, Mean ± s.d., n=3 biologically independent extracts, two-tailed paired Student’s t-test) or Western blotting analysis (b). (c) In vitro-synthesized biotinylated sense (S) or antisense (AS) NBR2 #1 were incubated with protein lysates from HEK293T cells transfected with various vectors as indicated. Precipitation reactions were conducted using streptavidin beads and then subjected to Western blotting. (d, f) In vitro-synthesized biotinylated sense (S) NBR2 or antisense (AS) NBR2 with different splicing isoforms were incubated with protein lysates from 786-O cells which had been cultured in 25 or 0 mM glucose-containing medium for 24 hours. Precipitation reactions were conducted using streptavidin beads and then subjected to Western blotting. (e) In vitro-synthesized biotinylated sense (S) or antisense (AS) NBR2 #1 were incubated with purified human AMPK α protein. Precipitation reactions were conducted using streptavidin beads and then subjected to Western blotting. (g) 786-O cells were cultured in 0 or 25 mM glucose-containing medium for 24 hours. Protein lysates were prepared and immunoprecipitated with AMPK α antibody or IgG. The RNA levels of NBR2 in immunoprecipitates or cell lysates (input) were measured by real-time PCR (Mean ± s.d., n=3 biologically independent extracts, two-tailed paired Student’s t-test). (h) In vitro-synthesized biotinylated NBR2 #1 were incubated with protein lysates from HEK293T cells transfected with various vectors and subjected to glucose starvation. Precipitation reactions were conducted using streptavidin beads and then subjected to Western blotting. Source data for a, g can be found in Supplementary Table 1. Unprocessed original scans of blots are shown in Supplemental Fig. 8.