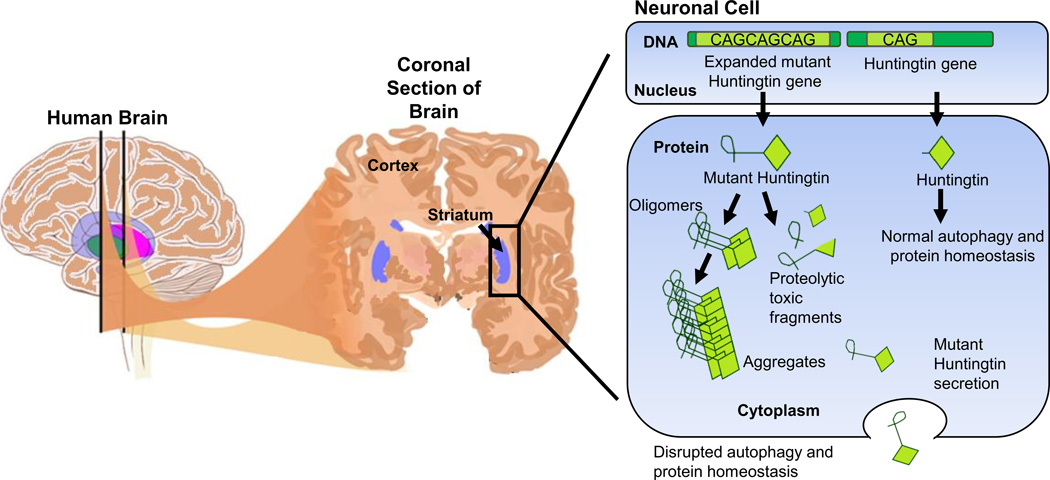
Figure 1. A schematic representation of the brain highlighting the striatum and the pathology of HD in a neuronal cell.
In affected neuronal cells, the mutant HTT gene with an expanded CAG trinucleotide tract is transcribed and translated to mutant HTT (mHTT) protein. mHTT protein does not fold correctly and forms aggregates and fragments which cannot be cleared properly from the cell and as a result is thought to cause certain disease phenotypes.