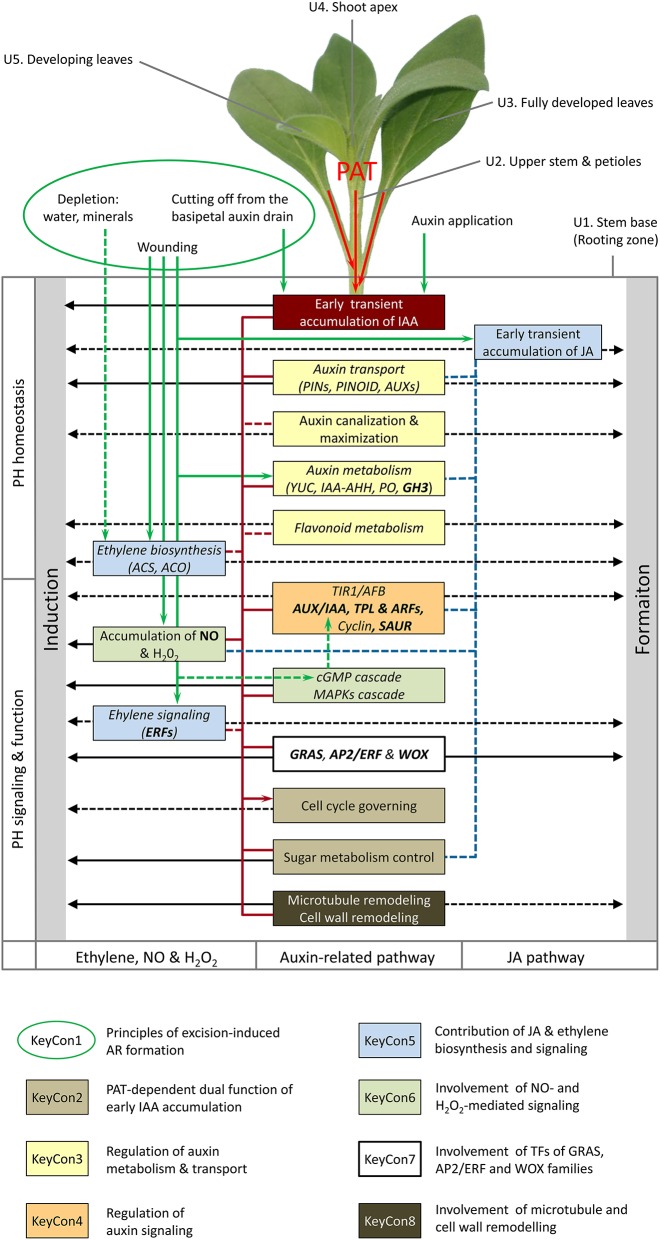
Figure 2.
General model of important physiological units of shoot tip cuttings and regulative factors controlling ethylene, auxin, and jasmonic acid homeostasis, signaling and function in AR formation. Factors underlying the Key Concepts 1–8 are indicated by specific framing and colors. Components with postulated phase-specific regulative character and crossroad functions between different plant hormones (PH) are indicated by italic and bold letters, respectively. Black arrows indicate evident or hypothetic (dashed lines) functions in induction and formation of ARs. Green arrows indicate evident (supported by data on cuttings) and hypothetic (supported by other data, dashed lines) factors stimulating accumulation of IAA (PAT-dependent), JA and NO, auxin biosynthesis and mobilization, and ethylene biosynthesis and signaling. Red lines indicate evident and hypothetic (dashed lines) linkages between components of ethylene and auxin biosynthesis, signaling and function. Blue dashed lines indicate linkages between JA and auxin homeostasis and signaling and invertase activation. Function of units (not complete): U1, rooting zone; U2, transport route of hormones and others; U3, carbohydrate source, potential source of auxin, U4, carbohydrate sink competing to the rooting zone (Klopotek et al., 2016), potential source of auxin; U5, carbohydrate sink, potential source of auxin. The scheme integrates the petunia model of Figure 1 and recent results obtained on other plant species, which are discussed in the text.