FIGURE 2.
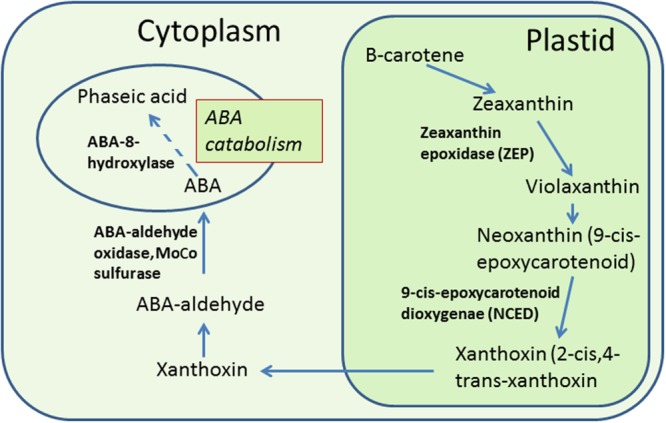
ABA biosynthesis in plant cells and its catabolism to phaseic acid. ABA is synthesized from carotenoids in a series of reactions in plastids and cytoplasm. In plastids, the carotenoids are converted to zeaxanthin and zeaxanthin to violaxanthin by enzyme zeaxanthin epoxidase (ZEP). Violaxanthin produces neoxanthin (9-cis-epoxycarotenoid) which is converted to xanthoxin (2-cis,4-trans-xanthoxin) by the oxidative cleavage of neoxanthin by the enzyme 9-cis epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase (NCED; Schwartz et al., 1997; see review by Seo and Koshiba, 2002). Xanthoxin is transported to the cytoplasm where it is converted to ABA by a two-step reaction. ABA is catabolized in cytoplasm to form phaseic acid. Enzyme names are shown in bold. Dotted lines indicate more than one reaction.
