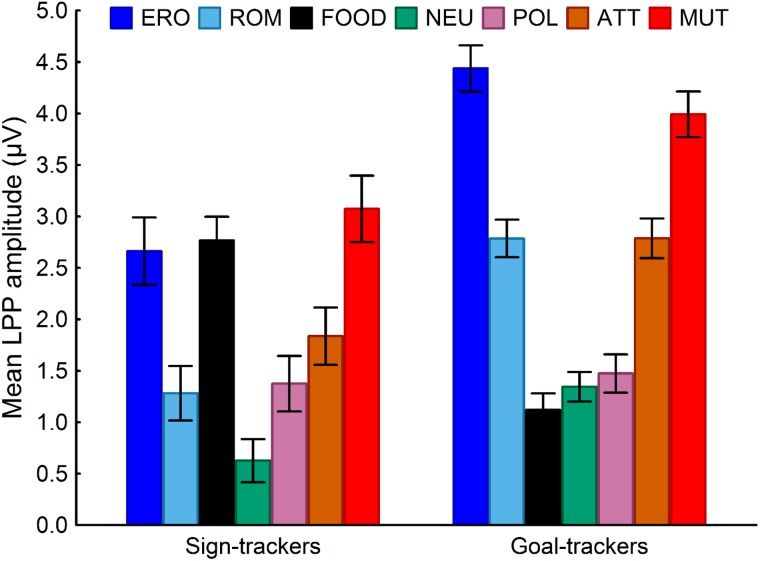
Fig. 3.
Brain reactivity to food and other emotional stimuli in sign trackers and goal trackers. The amplitude of the LPP to emotional stimuli uncovers endophenotypes associated with individual differences in the propensity to attribute incentive salience to reward-related stimuli: sign trackers react more to food-related stimuli than to pleasant stimuli (P < 0.005), goal trackers have the opposite pattern (P < 0.001). Note: ERO, erotica; ROM, romance; NEU, neutral; POL, pollution; ATT, attack; MUT, mutilations.