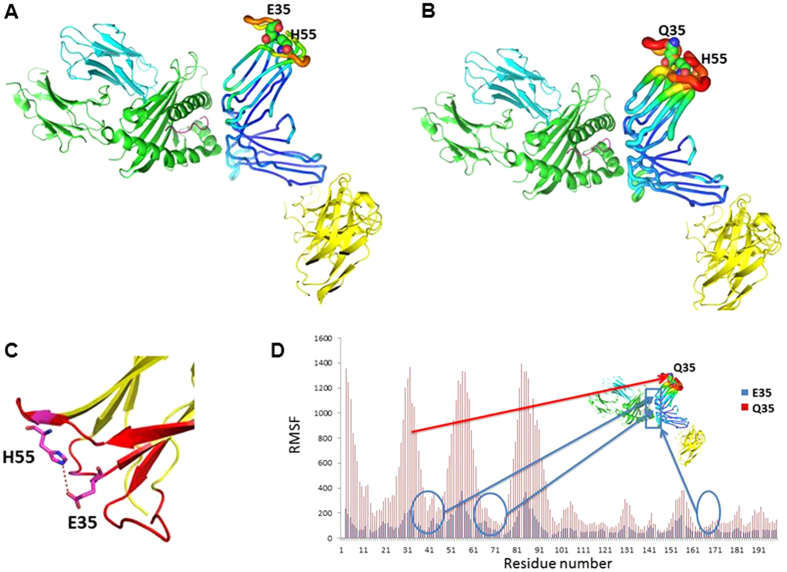
Figure 5. Structural effects of KIR2DL2-E35Q substitution.
The effects of E35Q substitution in KIR2DL2 in MD simulations are shown in (A) KIR2DL2*001-E35 and (B) KIR2DL2*001-Q35. KIR monomer binding to HLA ligand is shown in sausage representation. The other KIR monomer and HLA are shown in cartoon representation. Larger radii and warmer color indicate higher flexibility. Residues at positions 35 and 55 are shown in sphere. E35Q not only significantly destabilizes its adjacent regions but also substantially increases the flexibility of HLA binding interface. (C) E35 is predicted to form hydrogen bond with H55 side chain, which may contribute to the stabilization of the KIR2DL2-E35 structure. (D) E35Q causes significant conformational flexibility change of KIR2DL2, shown by much higher RMSF of the mutant. E35Q substitution in KIR2DL2 greatly destabilizes the adjacent regions of the protein, and changes the flexibility of KIR2DL2 and HLA ligand binding site. E35Q and other residues that are involved in KIR2DL2 and HLA ligand interaction are mapped to the KIR2DL2-HLA structure. The HLA binding site on KIR2DL2 is highlighted with a blue frame.