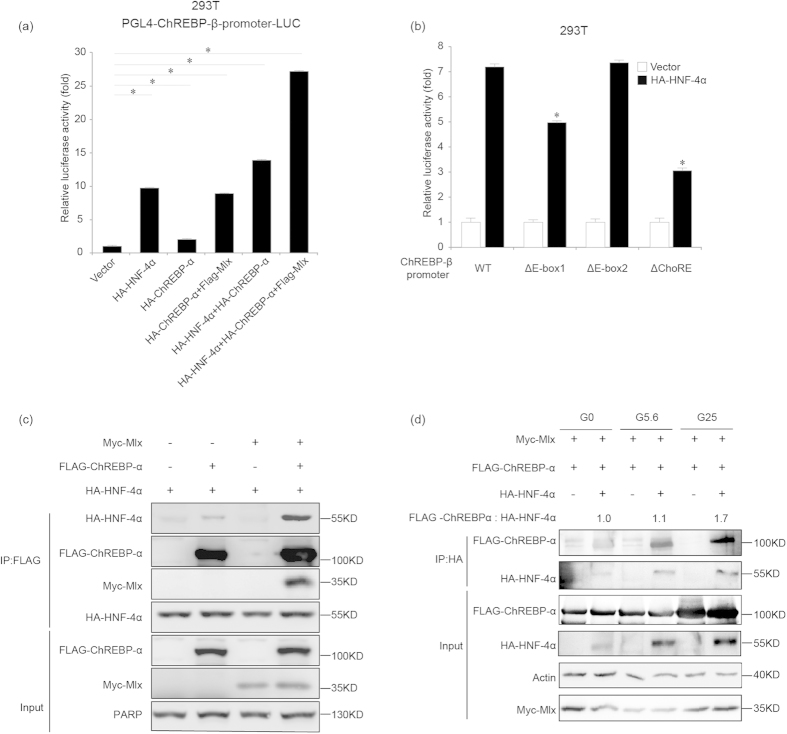
Figure 6. HNF-4α and ChREBP-α additively promote ChREBP-β transcription.
(a). Luciferase activity analysis for the 2.9 kb ChREBP-β promoter in the pGL4-Basic plasmid at 24 hours after the ChREBP-β promoter plasmid and empty vector or HA-HNF-4α or HA-ChREBP-α or HA-ChREBP-α and FLAG-Mlx or HA-HNF-4α and HA-ChREBP-α or HA-HNF-4α, HA-ChREBP-α and FLAG-Mlx expression plasmids are transfected in 293T cells. *indicates p < 0.05. (b). Luciferase activity analysis for the 2.9 kb (WT), ΔE-box1, ΔE-box2, and ΔChoRE ChREBP-β promoter in the pGL4-Basic plasmids at 24 hours after the ChREBP-β promoter plasmids and empty vector or HA-HNF-4α expression plasmid are transfected in 293T cells. *indicates p < 0.05 when compared with the empty vector-transfected sample. (c). Co-IP analysis for ectopically expressed ChREBP-α, HNF-4α and Mlx at 48 hours after transfection in 293T cells. Tubulin serves as the loading control. (d). Co-IP analysis for ectopically expressed ChREBP-α, HNF-4α and Mlx in 293T cells treated with 0 (G0), 5.6 (G5.6) or 25 mM glucose (G25) for 18 hours. Actin serves as the loading control. The intensity of bands has been measured and the ratio between immunoprecipitated FLAG-ChREBP-α and HA-HNF-4α is shown as fold of induction at G5.6 or G25 compared with G0.