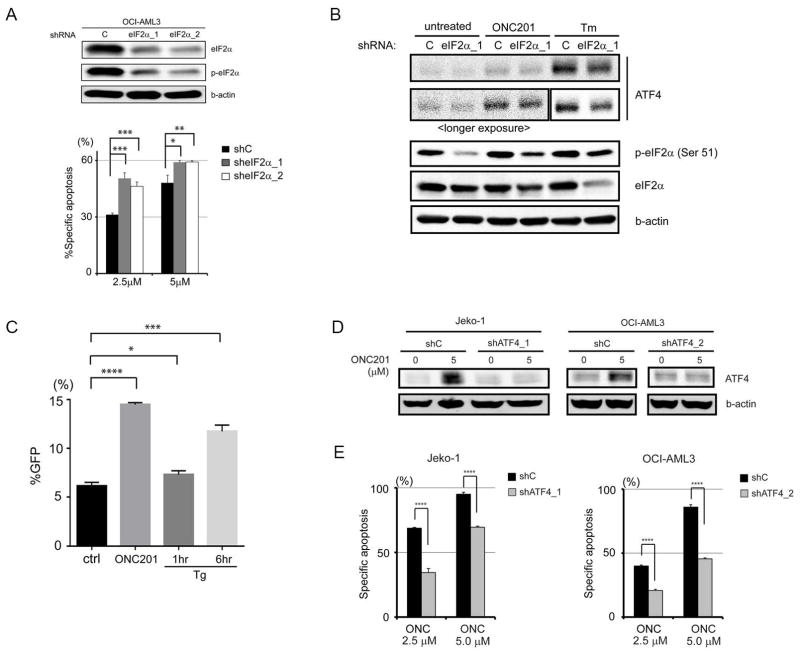
Fig. 6. ATF4 induction by ONC201 and its role in apoptosis.
(A) Immunoblot analysis of total and phosphorylated eIF2α in OCI-AML3 cells transfected with control shRNA and shRNAs against eIF2α (eIF2α_1 and eIF2α_2) and effects of eIF2α knockdown on apoptosis of cells treated with ONC201 (5 μM) for 72 hours. (B) Representative immunoblots (from three experiments) of ATF4 and eIF2α in OCI-AML3 cells transfected with control or eIF2α-targeting shRNA and treated with ONC201 (5 μM for 24 hours) or tunicamycin (Tm; 1 μM for 6 hours). (C) Green fluorescent protein (GFP) reporter assay of ATF4 translation. 4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI)–negative and GFP-positive cells were counted by flow cytometry after treatment with dimethyl sulfoxide (ctrl), ONC201 (5 μM for 27 hours), or thapsigargin (Tg; 1 μM for 1 or 6 hours) (n = 3 experiments). (D) Immunoblot verification of ATF4 knockdown in JeKo-1 (shATF4_1) and OCI-AML3 (shATF4_2) cells. (E) Specific apoptosis induced by ONC201 in control and ATF4 knockdown JeKo-1 (shATF_1) and OCI-AML3 (shATF_2) cells (n = 3 experiments). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.