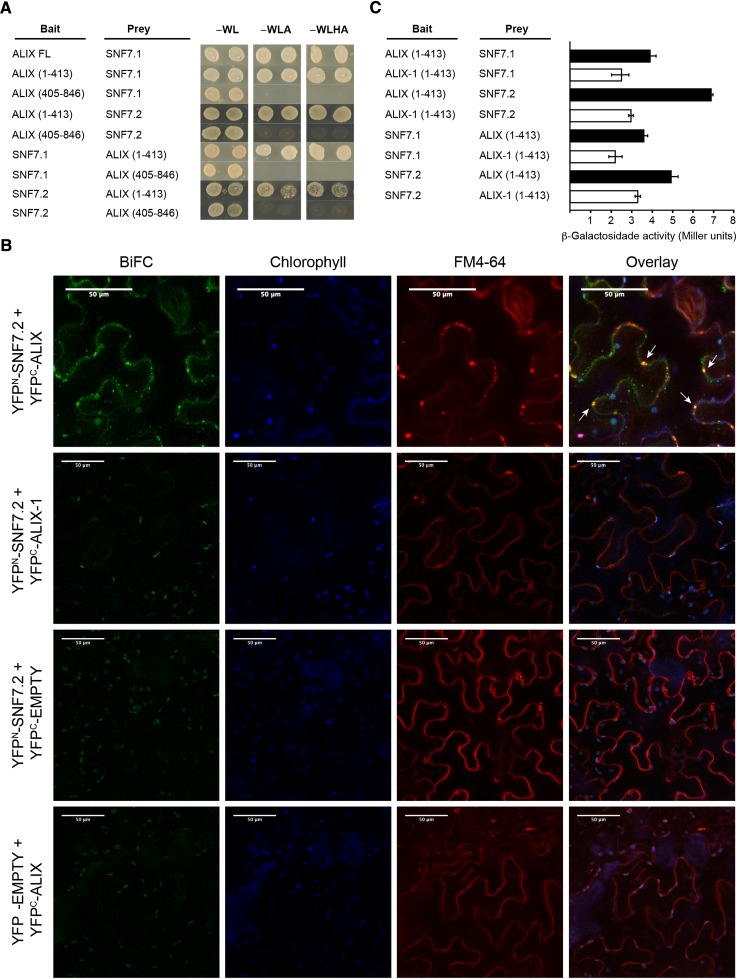
Figure 5.
ALIX Interacts with ESCRT-III Complex Component VPS32/SNF7 through Its Bro1 Domain.
(A) Yeast two-hybrid assays showing interaction between the Bro1 domain of At-ALIX and SNF7.1 and SNF7.2. ALIX full-length (FL) and truncated versions (comprising the Bro1 domain, amino acids 1 to 413; or the coiled coils plus the Pro-rich region, amino acids 405 to 846) were used. Transformed yeast cells were grown in SD-WL medium as a transformation control and in SD-WLA and SD-WLHA media for interaction assays.
(B) BiFC assays show that ALIX, but not a version containing the alix-1 mutation, interacts with SNF7.2 in vivo. FM-4-64 (5 μM) was injected in Nicotiana benthamiana leaf epidermal cells expressing different construct combinations as indicated. Leaves were observed by confocal imaging after 60 min. Reconstitution of YFP fluorescence indicates that the corresponding ALIX and SNF7 constructs directly interact. White arrows show YFP fluorescence colocalization with FM4-64 signal (red channel). Plastid autofluorescence due to chlorophyll is shown in the blue channel. Bars = 50 μm.
(C) alix-1 mutation reduces the ability of the Bro1 domain to interact with SNF7 proteins. β-Galactosidase assays were performed on yeast cotransfected with plasmids expressing indicated recombinant proteins. Error bars indicate standard deviations. n = 6.