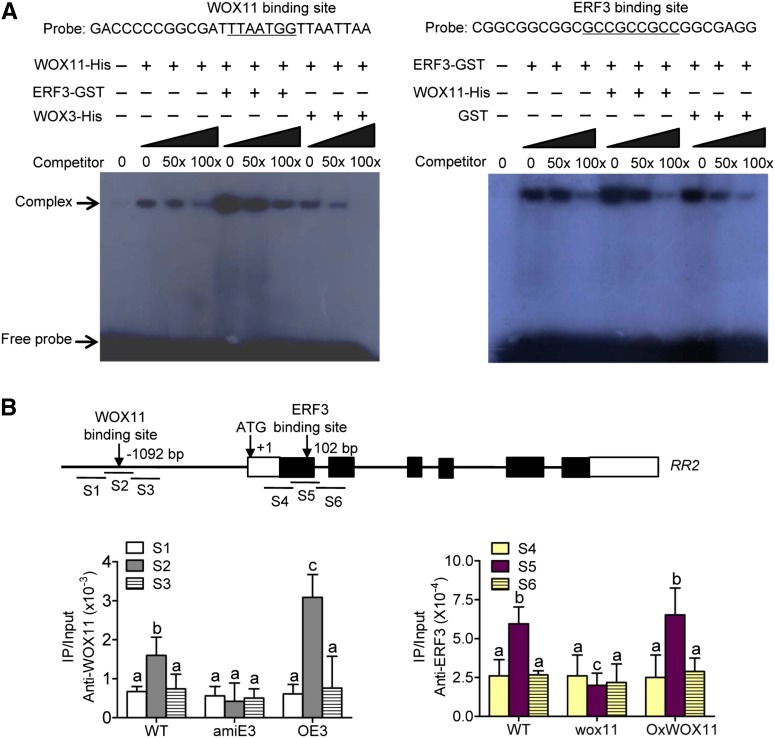
Figure 6.
ERF3 Promotes WOX11 Binding to RR2.
(A) Gel-shift assays of WOX11 binding to RR2 promoter containing the WOX11 binding site in the presence or absence of ERF3 (left) and ERF3 binding to RR2 first exon (P2) containing the ERF binding site in the presence or absence of WOX11 (right). E. coli-produced ERF3 and WOX11 proteins were incubated with 32P-labeled probes in the absence or presence of 50 or 100 M excess of the corresponding cold probes and analyzed by electrophoresis. The shifted band is indicated by the arrow. Three biological replicates were conducted.
(B) ChIP analysis of ERF3 and WOX11 binding to RR2 in different transgenic plants. Nuclei from OE3, amiE3, wox11, OxWOX11, and the wild type (WT) were immunoprecipitated by WOX11 (left) or ERF3 (right) antibodies. The precipitated chromatin fragments were analyzed by qPCR using six primer sets amplifying six RR2 regions (S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, and S6) as indicated. The relative nucleotide positions of the putative WOX11/ERF3 binding sites are indicated with arrows. One-tenth of the input (without antibody precipitation) chromatin was analyzed and used as control. Three biological replications were performed. Each value is the average ± sd from three independent experiments. Significant differences between samples (t test) are indicated by different letters.