Fig. 1.
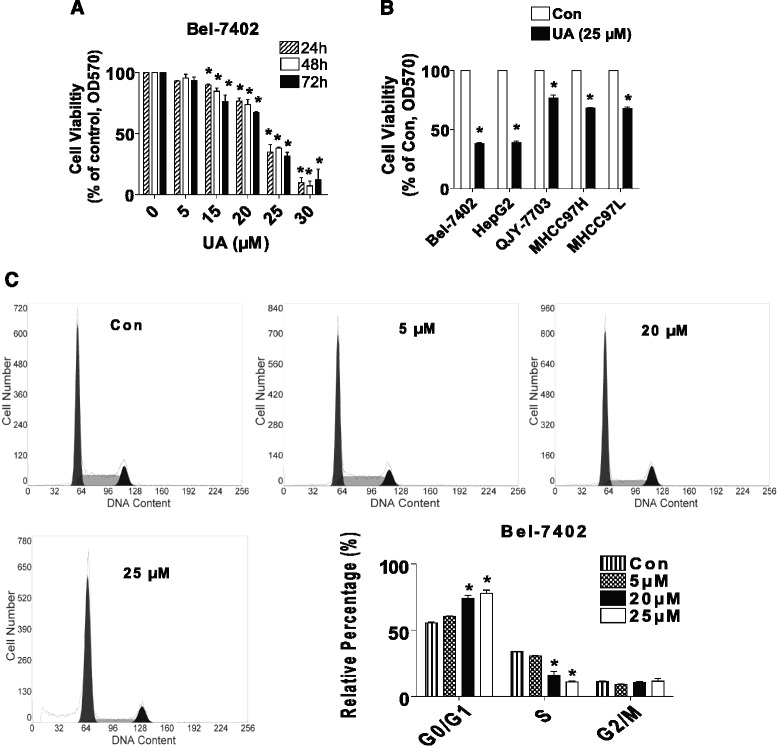
UA inhibited growth of HCC cells in the dose-dependent fashion. a, Bel-7402 cells were treated with increased concentrations of UA for up to 72 h to examine the cell viability. b, HCC cell lines indicated were treated with UA (25 μM) for 48 h. Afterwards, the cell viability was determined using the MTT assay as described in the Materials and Methods Section and was expressed as percentage of control in the mean ± SD of three separate experiments. *Indicates significant difference as compared to the untreated control group (P < 0.05). c, Bel-7402 cells were stimulated with different concentrations (e.g., 5, 20, 25 μM) of UA for up to 24 h. The cells were collected and processed for analysis of cell cycle distribution. Cell cycle was analyzed by flow cytometry after propidium iodide (PI) staining, and the percentages of the cell population in each phase (G0/G1, S and G2/M) of cell cycle were analyzed by Multicycle AV DNA Analysis Software. Data are expressed as a percentage of total cells. Values are given as the mean ± SD, from 3 independent experiments performed in triplicate. *Represents P < 0.05 versus control group
