Figure 3.
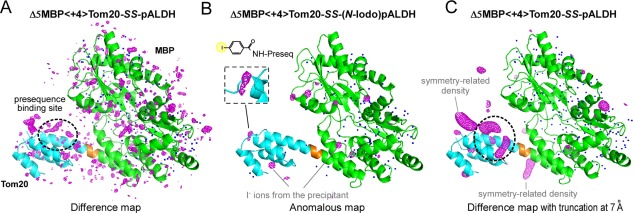
Electron density maps of the disulfide‐bond tethered MBP‐Tom20 complexes. (A) F o−F c difference electron density map of Δ5MBP<+4>Tom20‐SS‐pALDH, contoured at +3σ. (B) Anomalous difference map of Δ5MBP<+4>Tom20‐SS‐(N‐iodo)pALDH, contoured at +5σ to locate iodine atoms/ions. The inset shows an enlarged view of the electron density of the iodine atom in the 4‐iodobenzoyl group attached to the N‐terminus of pALDH. The electron densities of the bound iodine ions from the precipitant solution are also clearly visible, but their spherical shapes are easily discriminated from the iodine atom at the N‐terminus. (C) Difference map with truncation of high‐resolution reflections at 7 Å prior to Fourier transformation, contoured at +3σ. Note that the same X‐ray diffraction data set was used for map generation in (A) and (C). MBP and Tom20 are colored green and cyan, respectively. The 4‐residue spacer is colored orange. Water molecules included in the molecular replacement are depicted as blue dots.
