Figure 1.
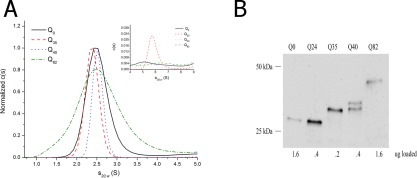
A: c(s) distribution for Qn‐YFP monomers in c. elegans assessed by sedimentation velocity analysis at high speeds (50,000 rpm) in 1x lysis buffer (50 mM HEPES, pH 7.3, 100 mM KCl, 2 mM PMSF, 10 mM DTT, 1 mM EGTA, and supplemented with protease inhibitor 1x PICS) at 20°C. The data were fitted using a c(s) continuous size distribution model (Sedfit v. 14.4d), commonly used to describe the behavior of small diffusing particles. Inset: focus on the 4‐9 S range shows a small amount of slightly aggregated sedimenting material. B: Western blot of Qn‐YFP in C. elegans using one‐day‐old adult worms. Loading concentrations have been adjusted to detect YFP in each of the samples. (Note: Supporting Information Figure S1A shows a Western blot of Qn‐YFP when the same amount of total protein is loaded per well.)
