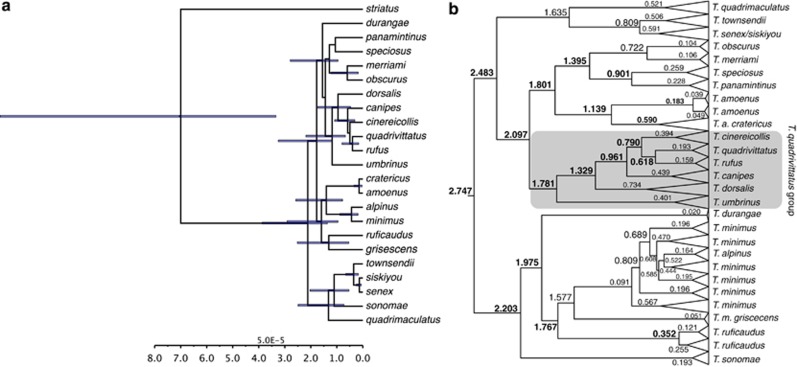
Figure 1.
Chronograms for 20 of 23 species of western chipmunks in the subgenus Neotamias (missing are T. bulleri, T. palmeri and T. ochrogenys) based on reanalysis of four nuclear genes (acrosin, zonadhesin, zona pellucida proteins 2 and 3) published by Reid et al. (2012). (a) Species-tree estimate derived using *BEAST from four nuclear loci reported in Reid et al. (2012). These four phased nuclear loci from individuals assigned to species based on bacular morphology were used to estimate a posterior distribution of species trees using *BEAST (Heled and Drumond, 2010). The analysis assumed an uncorrelated lognormal clock prior and birth–death tree prior. The MCMC chain was run for 50 000 000 generations and sampled every 5000 generations. The posterior distribution of species trees was summarized into a point estimate of topology using TreeAnnotator v1.7.5 (available: www.beast2.org/wiki/index.php/TreeAnnotator) after removing 1000 samples (10%) as a burn-in, setting a posterior probability threshold of 0.5 and using median node heights. The tree was visualized using FigTree v1.4.0 (available: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/), and the root has been rescaled to a depth of 7 Myr. (b) The concatenated tree was rooted with T. striatus and rescaled the root node to be 7 Myr based on Late Miocene date of Dahlquist et al. (1996). PartitionFinder 1.0.1 (Lanfear et al., 2012) was used to choose a partitioning scheme based on the Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC) that placed zonadhesin, zona pellucida protein 2 and zona pellucida protein 3 under a K80+I+Γ model of sequence evolution and acrosin under an HKY+Γ model of sequence evolution. A posterior distribution of topologies was generated using BEAST 1.7.4 (Drummond et al., 2012). We ran two independent runs of 50 000 000 generations and sampled every 5000 generations. Convergence was assessed by comparing traces, comparing posterior distributions of parameter estimates and ensuring the effective sampling size of each parameter was at least 200 or greater. The two runs were then combined using LogCombiner (available: https://github.com/SeleniumHQ/selenium/blob/.../LogCombiner.java) after removing 10% of the samples as a burn-in. A maximum clade credibility tree was generated using TreeAnnotator from the combined distribution of topologies with a posterior probability threshold of 0.5 and median node heights. Associated with nodes are divergence times (in Myr), and those in bold font are nodes that span introgression events. Shaded taxa represent the T. quadrivittatus group.