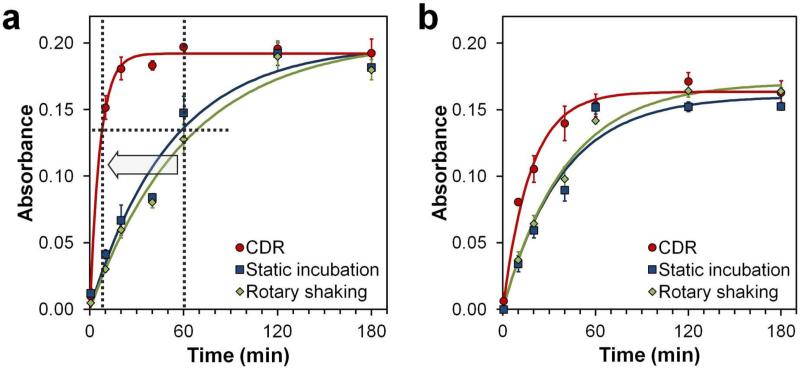
Figure 2.
Kinetics of rapid ELISA diagnostics. (a) Assay performed with Poly-HRP probes exhibited slow mass transfer-limited kinetics under static incubation (t½ = 36 min) and rotary shaking (t½ = 43 min) conditions, but demonstrated a dramatically improved performance with CDR (t½ = 5 min). Compared to standard ELISA protocols where incubation typically takes 1 h, CDR reaches the same staining intensity in 7 minutes. (b) Smaller mono-HRP probes exhibited faster kinetics under static incubation (t½ = 26 min) and rotary shaking (t½ = 28 min) conditions, featuring further improvement in assay speed with CDR (t½ = 12 min). Solution absorbance at 450 nm with respect to assay time is shown and fitted by an exponential curve. Background absorbance by the TMB substrate alone was subtracted from all measurements. Error bars represent one standard deviation from triplicate assays.