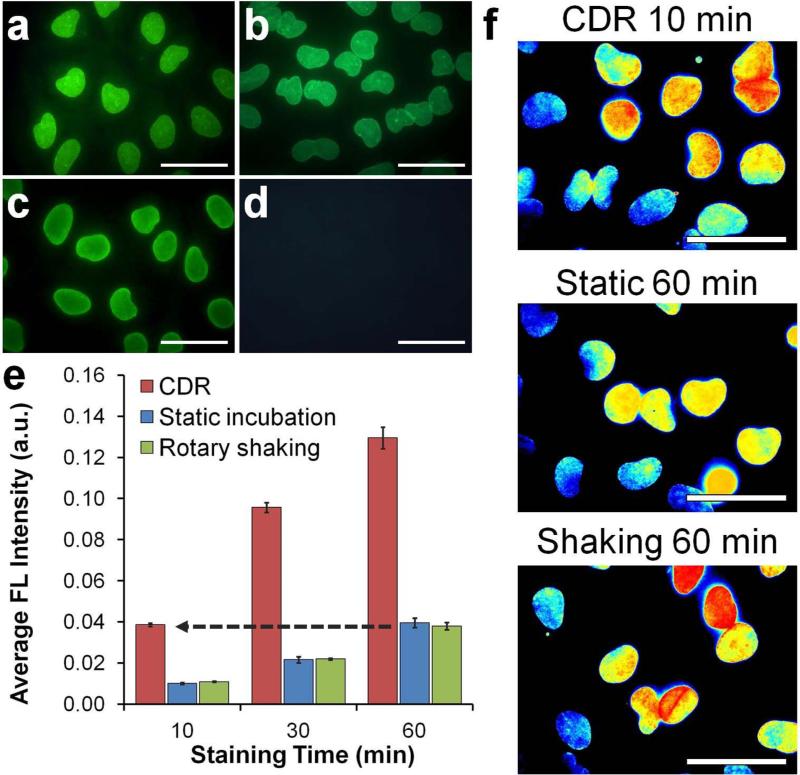
Figure 3.
Rapid immunofluorescence staining with QDot probes. (a-d) Characterization of QDot-1'Ab and dye-labeled 1'Ab probes targeting Lamin A. One-step immunofluorescence images obtained with (a) QDot-1’Ab and (b) dye-labeled 1’Ab probes produced staining patterns consistent with the nuclear membrane localization of Lamin A and (c,d) results obtained with QDot-2'Ab in a conventional two-step staining procedure (positive Lamin A staining is shown in (c) and control lacking 1’Ab incubation in (d)). Scale bar, 50 μm. (e) Quantitative evaluation of staining intensity with respect to staining time achieved via CDR, static incubation, and rotary shaking techniques. Notably, CDR achieved comparable staining intensity 6 times faster than conventional methods, producing detectable signal within the first 10 minutes of staining. Error bars represent one standard deviation of an average Lamin A staining intensity from four different fields of view. (f) Representative cell staining intensity maps obtained after 10-min CDR in comparison to 60-min static and rotary shaking incubation. All images were normalized and color-coded with a heat map for direct comparison of staining pattern and intensities. Scale bar, 50 μm.