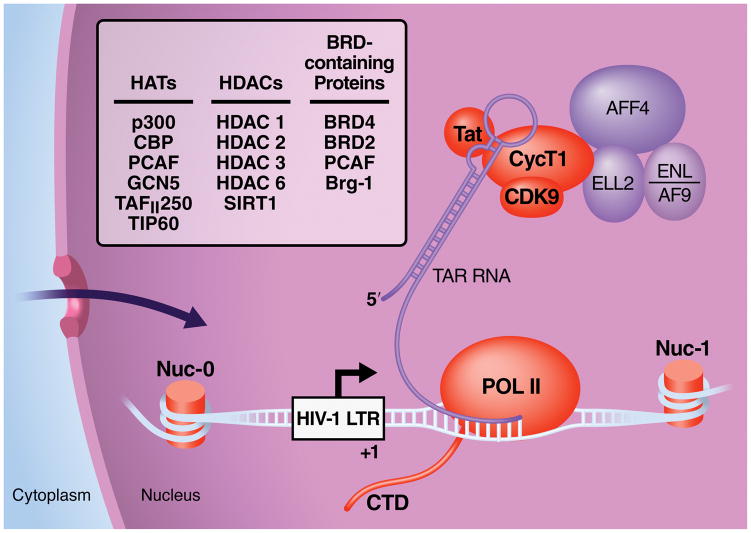
Figure 4. Regulation of HIV transcription by protein acetylation.
HIV transcription is closely associated with the host acetylation machinery and is currently a target for acetyllysine-targeting drug regimens. Viral (Tat) and host factors (histones in nucleosomes (nuc), the Tat cofactor P-TEFb, RNA polymerase II (POL II)) that are targets of acetylation are depicted in orange. HATs, HDACs and bromodomain (BRD)-containing factors associated with HIV transcription are listed in the box. Proteins in purple depict factors of the super elongation complex (SEC) recently identified as interacting with P-TEFb and Tat. See text for details.