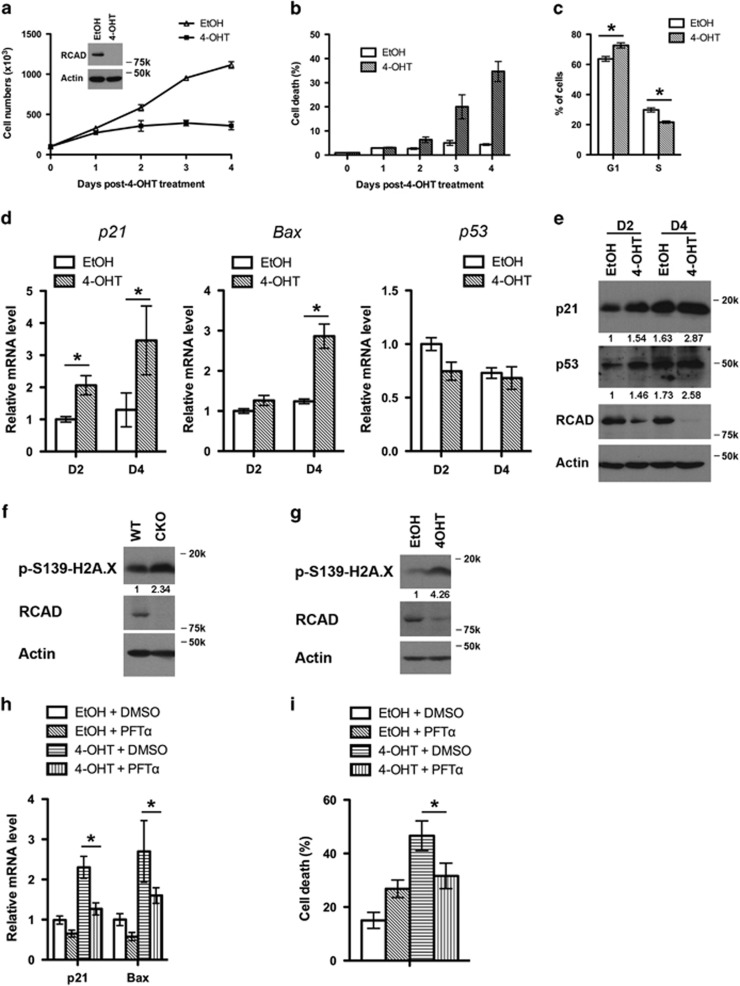
Figure 5.
Loss of RCAD leads to p53 activation and cell death of HSCs. (a) Proliferation of wild-type and RCAD-deficient HSCs. HSCs were sorted from BM of RCADF/F:CreERT2 mice, and cultured in the absence or presence of 4-OHT (1 μM) for indicated period of time. Cell numbers were manually scored. The experiment was performed three times independently. (b) Cell death of RCAD-deficient HSC cells. Cell death was elevated by DNA dye exclusion assay. (c) Cell cycle profile of RCAD-deficient HSCs. Cell cycle profile of HSCs was analyzed by PI staining after 4-day treatment of either EtOH or 4-OHT (1 μM). *P<0.01 (n=3). (d) Upregulation of p21 and Bax genes in RCAD-deficient cells. Relative mRNA levels of p21, Bax and p53 were evaluated by RT-PCR analysis. *P<0.01 (n=3). (e) Immunoblotting of p21 and p53 in EtOH and 4-OHT-treated HSCs. HSCs were harvested at indicated time points, and subjected to immunoblotting of p21, p53, RCAD and β-actin. (f) Phosphorylation of H2A.X in RCAD-deficient BM cells. After tamoxifen treatment, BM cells from either RCADF/F (WT) or RCADF/F:CreERT2 (CKO) mice were harvested. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting of indicated antibodies. (g) Phosphorylation of H2A.X in RCAD-deficient HSCs. Sorted HSCs were treated with either EtOH or 4-OHT (1 μM) for 2 days. (h) The effect of PFT-α on induction of p21 and Bax in RCAD-deficient HSCs. HSCs were cultured in the media containing indicated reagents (4-OHT, 1 μM; PFT-α, 10 μM) for 4 days and harvested. Total RNA was isolated and subjected to RT-PCR analysis. The results were normalized to the mRNA levels of p21 and Bax in HSCs treated with solvent (EtOH and DMSO), respectively. *P<0.01 (n=3). (i) The effect of PFT-α on cell death of HSCs. HSCs were cultured in the media containing indicated reagents (4-OHT, 1 μM; PFT-α, 10 μM) for 4 days, and cell death was scored by DNA dye exclusion assay. *P<0.01 (n=3). Data are presented as means±S.D.