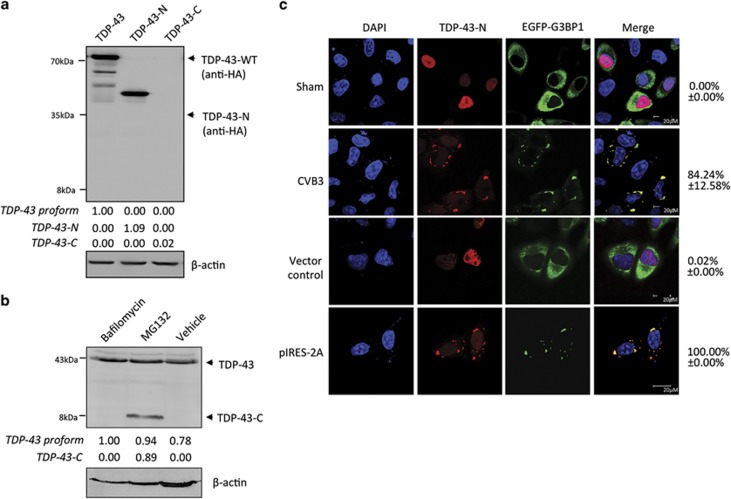
Figure 6.
TDP-43-C is rapidly degraded by the proteasome pathway and TDP-43-N localizes to stress granules to form protein aggregates after CVB3 infection. (a) Protein expression of full-length and truncated forms of TDP-43. HeLa cells were transiently transfected with HA-TDP-43-GFP, HA-TDP-43-N, or HA-TDP-43-C as indicated. Protein expression of various types of TDP3 was detected using an anti-HA antibody. The level of β-actin was examined as a loading control. (b) TDP-43-C is degraded through the proteasome pathway. HeLa cells were transiently transfected with HA-TDP-43-C in the presence of 200 nM bafilomycin (a lysosome inhibitor), 1 μM MG132 (a proteasome inhibitor), or equal volume of DMSO as a vehicle control for 24 h. Western blotting was performed using an anti-C-terminal TDP-43 antibody which detects both endogenous TDP-43 (~43 kDa) and exogenous HA-TDP-43-C (~8 kDa). Densitometric analysis of TDP-43 proform, TDP-43-N and TDP-43-C was carried out as in Figure 1. (c) Cytoplasmic localization and aggregation of TDP-43-N following either CVB3 infection or viral protease 2A expression. HeLa cells were transiently co-transfected with HA-TDP-43-N and EGFP-G3BP1 for 24 h, followed by either CVB3 infection for 3 h or second-round of transfection with viral protease 2A as indicated. Immunostaining was performed for the detection of TDP-43-N using anti-HA antibody (Alexa-fluor-594, red). Cell nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). GFP signal of EGFP-G3BP1 is shown in green. Percentage of cells expressing cytoplasmic TDP-43 was quantified as in Figure 4