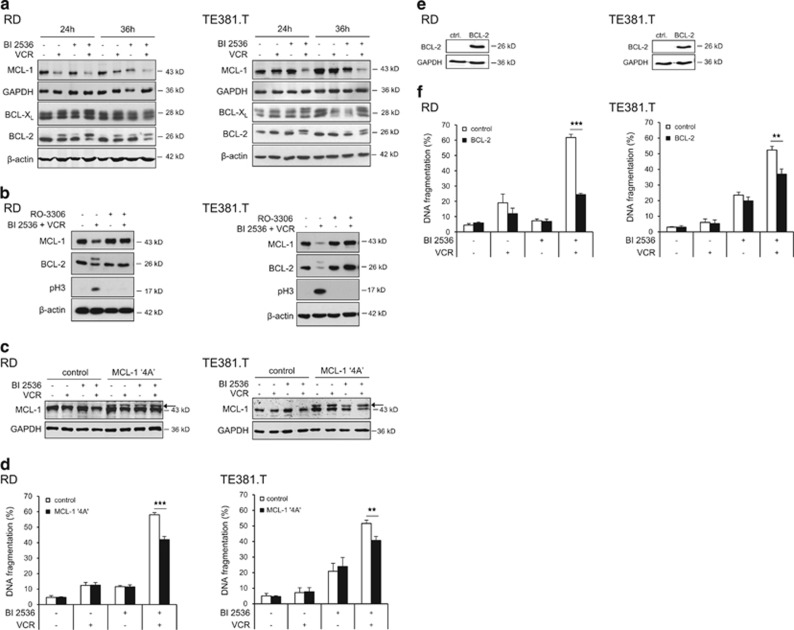
Figure 4.
Modulation of antiapoptotic BCL-2 proteins by BI 2536/VCR co-treatment. RD cells were treated with 4 nM BI 2536 and/or 2 nM VCR, TE381.T cells with 7 nM BI 2536 and/or 1 nM VCR for indicated time periods. (a) Protein expression of MCL-1, BCL-2 and BCL-XL was determined at 24 and 36 h by western blotting (n=3). β-Actin or GAPDH served as loading controls. (b) RD and TE381.T cells were pretreated for 1 h with 10 μM of CDK1 inhibitor RO-3306. Expression of the antiapoptotic BCL-2 family proteins MCL-1 and BCL-2 and mitotic marker pH3 was analyzed by western blotting (n=3). β-Actin served as loading control. (c and d) Cells were genetically engineered to stably express a non-degradable phospho-defective mutant of MCL-1 (MCL-1 ‘4A'). Expression of MCL-1 ‘4A' (indicated by arrow) in transfected RD and TE381.T cells was confirmed by western blotting at 24 h upon treatment with BI 2536 and/or VCR (n=2). GAPDH served as loading control (c). Apoptosis was analyzed by quantification of DNA fragmentation at 48 h (n=3) (e). (e and f) Cells were genetically engineered to stably express high levels of murine BCL-2. Overexpression of murine BCL-2 in transduced RD and TE381.T cells was confirmed by western blotting using an antibody that specifically detects murine BCL-2 (n=3). GAPDH served as loading control (e). Apoptosis was analyzed by quantification of DNA fragmentation at 48 h (n=3) (f). Cells transfected with corresponding empty vectors served as controls. Results are expressed as mean+S.D. (error bars) or representative blots are shown. Student's t-test was used to calculate two-sided P-values. **P<0.01; ***P<0.001