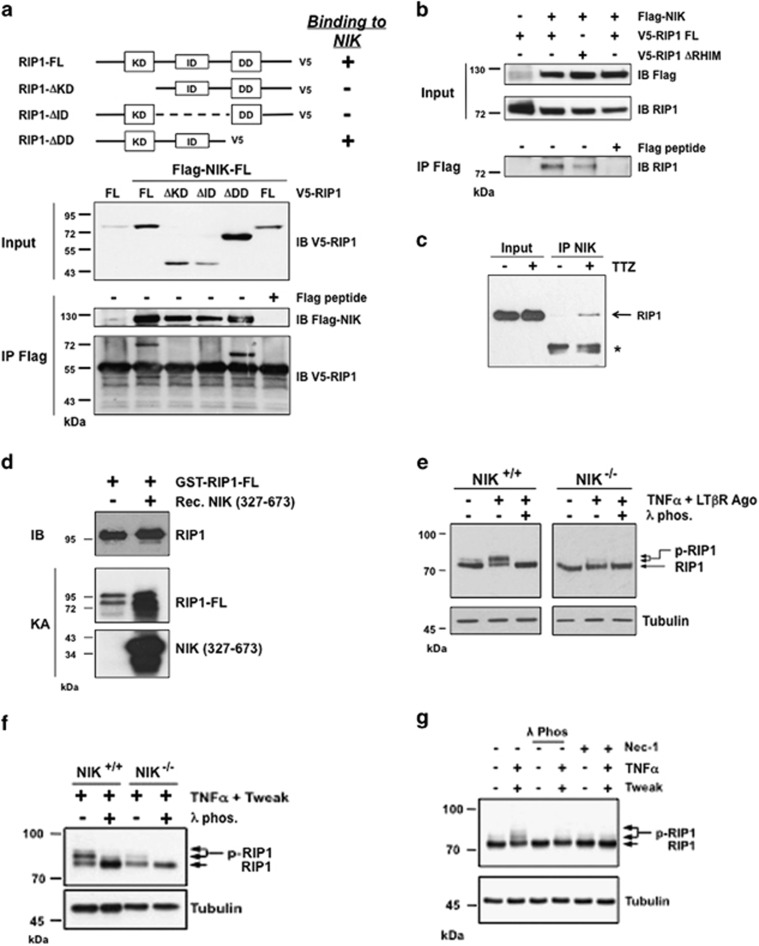
Figure 3.
NIK is a bona fide kinase of RIP1 in vivo and in vitro. (a) HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with expression vectors encoding full-length Flag-NIK-FL kinase dead together with either kinase dead RIP1-FL, truncated kinase domain (ΔKD) RIP1, truncated intermediate domain (ΔID) RIP1 or truncated death domain (ΔDD) RIP1. Flag immunoprecipitates were loaded on SDS-PAGE for detection of RIP1-V5. As control, anti-Flag immunoprecipitations were carried out in the presence of Flag peptide. (b) The same cells were transiently transfected with expression vectors encoding Flag-NIK-FL and FL kinase dead RIP1-V5 or ΔRHIM RIP1-V5 expression vectors. Flag-NIK-FL complexes were immunoprecipitated using an anti-Flag antibody, and RIP1 interactions were revealed by western blotting anti-RIP1. As control, anti-Flag immuniprecipitations were carry out in the presence of Flag peptide. (c) Mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) WT were treated or not with Tweak/TNFα and z-VAD (TTZ) and NIK-immunoprecipitates were analyzed by western blotting for the presence of endogenous RIP1. (d) In vitro kinase assays with recombinant NIK kinase domain (327–673) and active recombinant GST-RIP1 FL. (e) NIK+/+ and NIK−/− MEFs were left untreated or treated with a mix of TNFα and LTβR agonist antibody (Ago). The phosphorylation status of RIP1 was visualized by western blotting with cell extracts treated or not with the lambda phosphatase (λ phos.). (f) NIK+/+ and NIK−/− MEFs were treated with a mixture of TNFα and Tweak and analyzed similar to panel (e). (g) MEFs WT were treated with Tweak/TNFα in the absence or presence of Nec-1, and the protein extracts were analyzed by western blotting for RIP1 phosphorylation