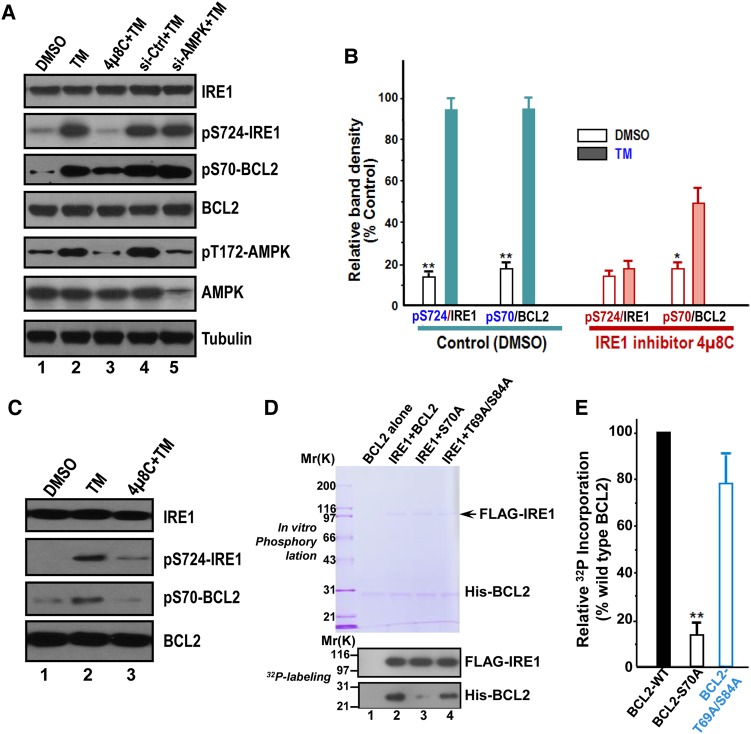
Figure 6.
ER stress preconditioning elicits BCL2 phosphorylation at Ser70 via IRE1. (A) Western blots of IRE1, phospho-Ser724 IRE1 (pS724-IRE1), phospho-Ser70 BCL2 (pS70-BCL2), BCL2, phospho-Thr172 AMPK (pT172-AMPK), and tubulin in HepG2 cells exposed to treatments as indicated. TM treatment induces phosphorylation of IRE1, AMPK, and BCL2. Note that pS70-BCL2 is a function of IRE1, as inhibition of IRE1 by chemical inhibitor 4µ8C abolished the phosphorylation of BCL2 in response to TM treatment. (B) Quantification of A from three independent experiments. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. (C) Western blots of IRE1, pS724-IRE1, pS70-BCL2, and BCL2 in L02 cells exposed to treatments as indicated. TM treatment induces phosphorylation of IRE1 and BCL2. Note that pS70-BCL2 is a function of IRE1, since inhibition of IRE1 by chemical inhibitor 4µ8C abolished the phosphorylation of BCL2 in response to TM treatment as it did in HepG2 cells. (D) BCL2 is a substrate of IRE1. Aliquot of recombinant hexa-histidine-tagged BCL2 (wild type and non-phosphorylatable mutants) were incubated with FLAG-IRE1 in the presence of 32P-ATP as detailed in Materials and methods. Upper panel is a representative Coomassie blue-stained gel and lower panel is the autoradiograph of a representative X-ray film. (E) Quantification of D from three independent phosphorylation experiments. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. **P < 0.01.