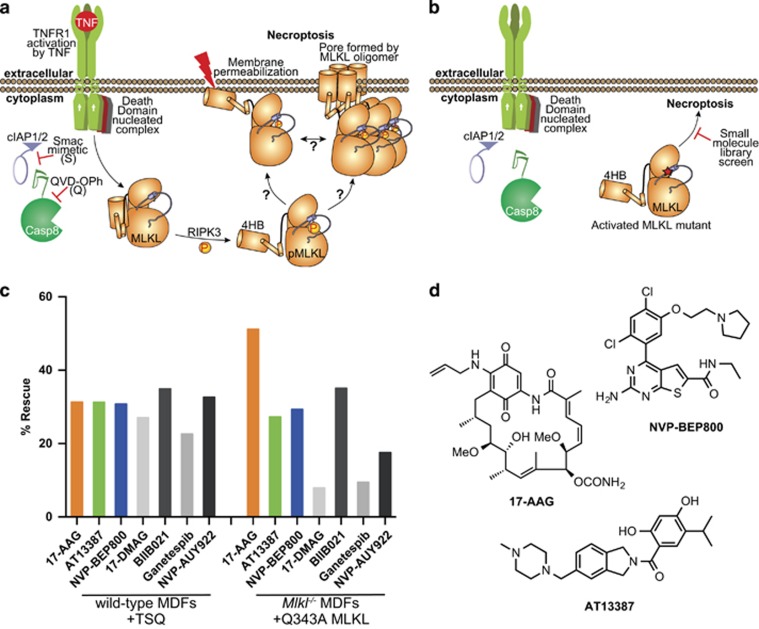
Figure 1.
Hsp90 inhibitors can block necroptosis downstream of MLKL activation. (a) A schematic of the necroptosis pathway. TNF (T) stimulates the TNFR1; cIAP1/2 activity is blocked with Smac mimetic (S); and the pan-caspase inhibitor, QVD-OPh (Q), blocks caspase-8 activity. This leads to RIPK3 activation and subsequent phosphorylation and activation of MLKL. (b) The activated MLKL mutant Q343A initiates cell death in the absence of TSQ stimulation or RIPK3 activation enabling a screen for inhibitors of necroptosis downstream of MLKL activation. (c) Cells were pretreated for 2 h with a library of 438 compounds with annotated mechanisms of action at 1 μM, then necroptosis was stimulated in wild-type MDFs with TSQ and expression of Q343A MLKL was induced in Mlkl−/− MDFs with doxycycline. Percentage rescue was determined using a CellTiter Glo assay, and normalised against TSQ/doxycycline stimulation and DMSO treatment. The data represent the HSP90 hits from each screen, and are the average of two technical replicates. (d) Chemical structures of the three compounds selected for further analysis