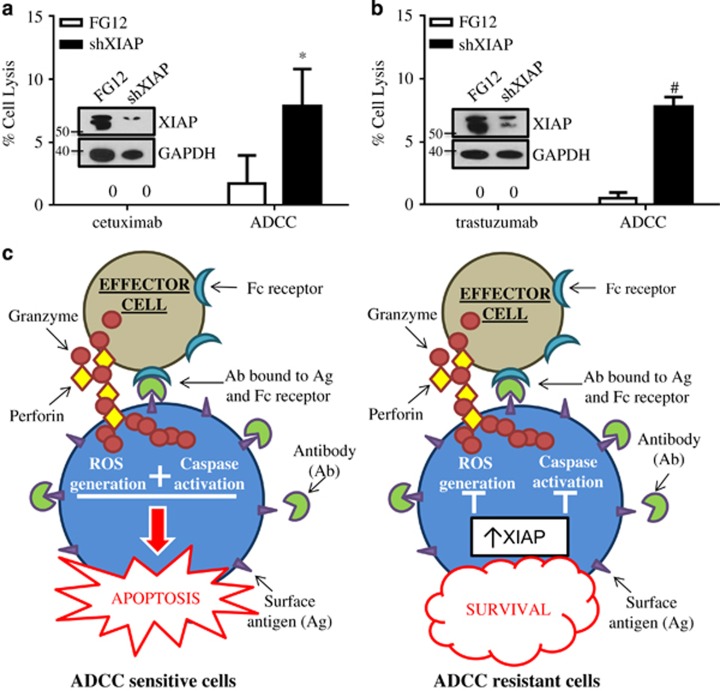
Figure 6.
Targeted inhibition of XIAP by RNAi sensitizes ADCC-resistant cells to apoptosis. Percent cell lysis of FG12 (control) or XIAP short hairpin RNA-transfected (a) rSUM149 cells and (b) rSUM190 cells incubated with antibody alone or ADCC conditions for 4 h. Bars represent mean±S.E.M. calculated percent lysis, n=4–5, *P<0.05, #P<0.001. Inset: Western immunoblot of XIAP expression at time of ADCC experiment. (c) Schematic of XIAP-mediated inhibition of ADCC. In ADCC-sensitive cells, antibody binding to surface antigen bridges tumor cells to effector cells, leading to subsequent release of lytic granules containing perforin and granzymes. Granzymes enter target cells through perforin channels, inducing both ROS generation and activating effector caspases leading to efficient apoptosis in tumor cells. In cells with XIAP overexpression, however, this process is abrogated through caspase-dependent and -independent mechanisms leading to tumor cell survival