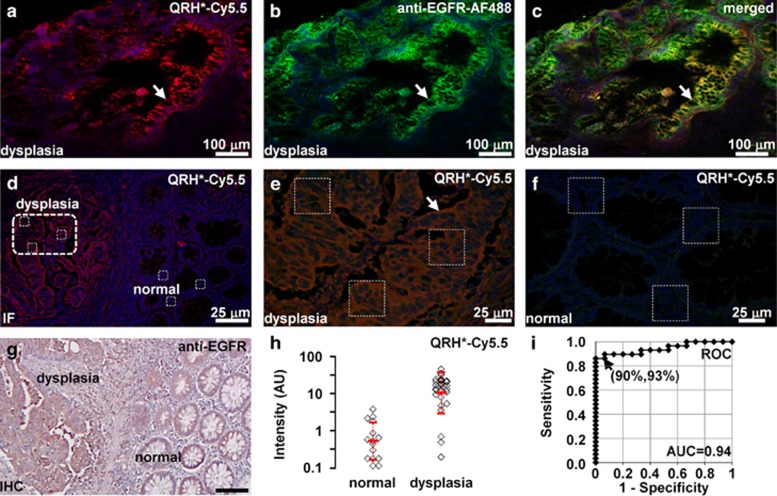
Figure 6.
Binding of EGFR peptide and antibody to human colonic neoplasia. On confocal microscopy, binding of (a) QRH*-Cy5.5 peptide (red) co-localizes with that of (b) AF488-labeled anti-EGFR antibody (green) on surface of dysplastic colonocytes (arrow), shown in (c) merged image, P=0.71. (d) Image contrast can be appreciated at lesion border. Magnified view of boxes in d is shown for (e) dysplasia and (f) normal. (g) Corresponding immunohistochemistry from a shows increased reactivity for EGFR in dysplasia. (h) Dysplasia (n=29) showed significantly higher fluorescence intensities than normal (n=15) by an average of 19.4-fold, P=1.7 × 10−9 by two-sample t-test on log-transformed data. (i) Receiver operating characteristic curve shows 90% sensitivity and 93% specificity with area under curve (AUC) of 0.94 for distinguishing dysplasia from normal using peptide.