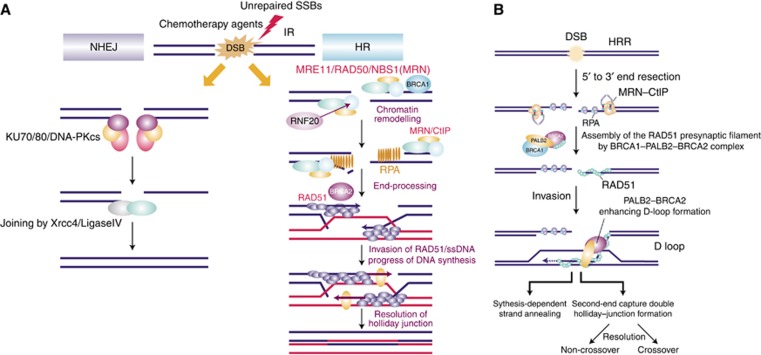
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair. Double-stranded breaks in DNA are typically repaired through one of two pathways: (A) non-homologous end joining (NHEJ); (A, B) homologous recombination (HR). Proteins involved in NHEJ include KU70/80, DNA-PKcs, XRCC4 and DNA ligase IV. Proteins involved in HR include MRE11, RAD50 and NBS1 (which form the MRN complex); CtIP; RNF20; RPA; RAD51; PALB2; BRCA1 and BRCA2. Abbreviations: HRR, homologous recombination repair; IR, ionising radiation; SSB, single-strand break; ssDNA, single-stranded DNA. Note: (A) Reproduced with permission from Pioneer Bioscience Publishing Company (© Saito et al, 2013). (B) Reprinted with permission from Nature America, Inc. (© Buisson et al, 2010).