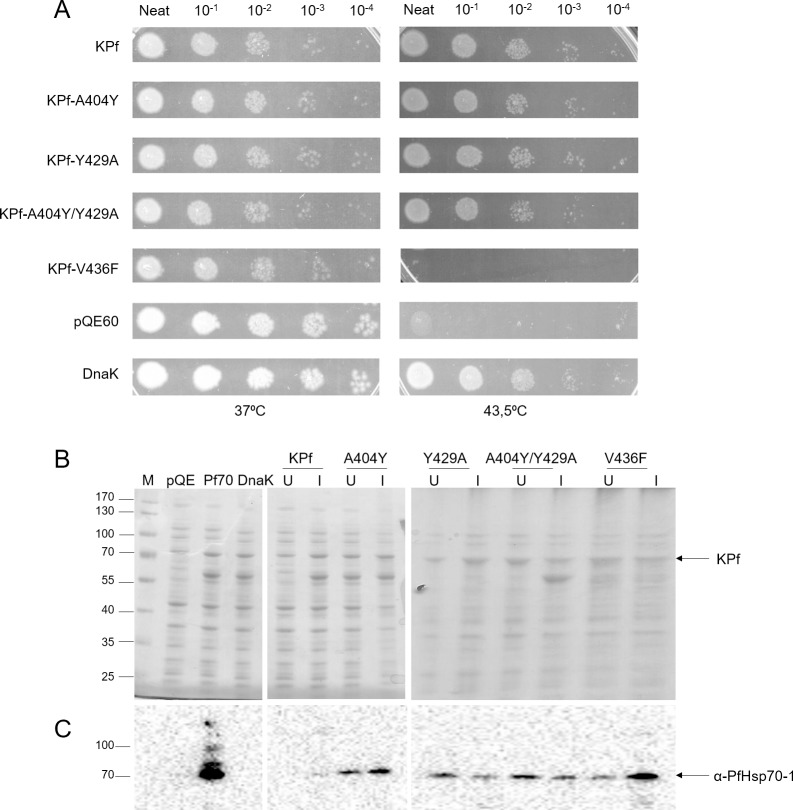
Fig 2. The hydrophobic pocket mutation abrogates the function of KPf.
(A) E. coli dnaK756 cells transformed with plasmid constructs expressing KPf and its substrate binding cavity mutants were incubated at 37°C and 43.5°C, respectively. The negative control consisted of cells transformed with pQE60 plasmid vector whilst the positive control was represented by cells transformed with the pQE60/DnaK plasmid. (B) SDS-PAGE and Western analyses for the exogenous expression of KPf and the respective substrate binding cavity derivatives in E. coli dnaK756 cells. Cells transformed with plasmid vector (pQE60) were used as negative control. The labels on the top of the gel panels represent the different proteins that were expressed as well as the vector control (pQE60). In each case, the left and right hand side lanes represents the sample that was taken before induction and 5 hours after induction with 1 mM IPTG, respectively. Numbers on the left handside represent protein markers (Fermentas) in kDa.