Figure 7.
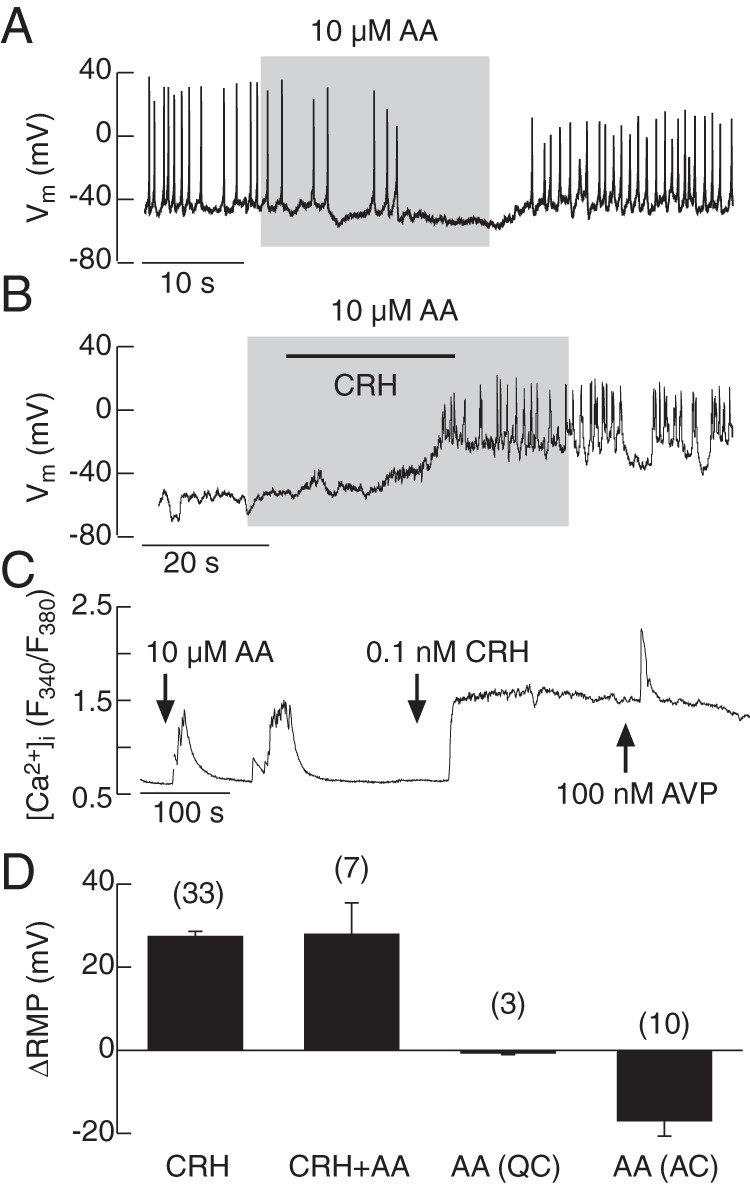
Effects of AA on spontaneous and CRH-induced electrical activity (A and B) and calcium signaling (C). AA induced hyperpolarization and inhibited APs in spontaneously firing corticotrophs (A). In quiescent cells in the presence of AA, CRH was able to depolarize the cell membrane and initiate AP firing (B). CRH facilitated Ca2+ influx in the presence of AA (C). Effects of CRH alone and in the presence of AA as well as AA alone in quiescent cells (QCs) in spontaneously active cells (ACs) on RMP; mean ± SEM values.
