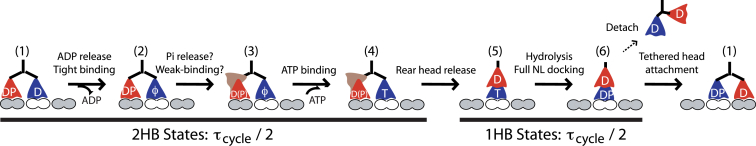
Figure 5.
Consensus kinesin-1 chemomechanical cycle. Upon tethered head binding (State 1), ADP release is rapid, generating a 2HB state with an apo front head (State 2). The rear head then transitions into an ATP waiting state (State 3), a transition that may involve Pi release and may involve a different interaction with the microtubule but does not cause a displacement. Upon ATP binding (State 4), the rear head rapidly detaches and moves forward 8 nm (State 5). ATP hydrolysis results in a vulnerable 1HB state (State 6) in which the bound head can detach to terminate the run or the tethered head can attach to complete the step. At physiological ATP, the cycle duration (τcycle) is split evenly between 1HB and 2HB states; as ATP is reduced the 2HB duration increases (11). To see this figure in color, go online.