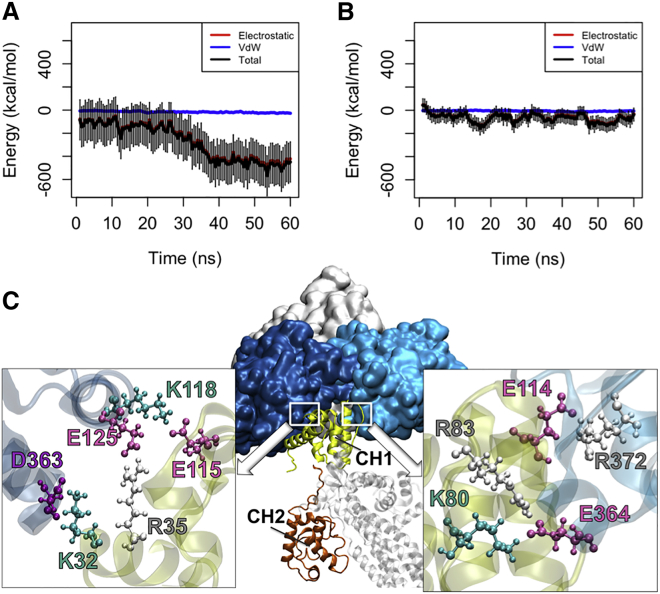
Figure 3.
The interaction between different ABD conformations and actin. (A) The CH1 domain of the oABD associated with actin after 30 ns with the final interaction energy of 550 kcal/mol averaged over three trials in the OW simulations. The interaction was stable for the last 20 ns of all trials. (B) On the contrary, the CH1 domain of the cABD did not strongly associate with actin within the 60 ns of simulation. (C) The interfaces between CH1 (yellow) of the oABD and two proximal actin monomers (blue) in the OW simulations are shown after 60 ns. Residues involved in all three salt bridges formed between CH1 and each actin monomer are highlighted (colors: arginine, white; lysine, turquoise; glutamic acid, pink; aspartic acid, purple). To see this figure in color, go online.