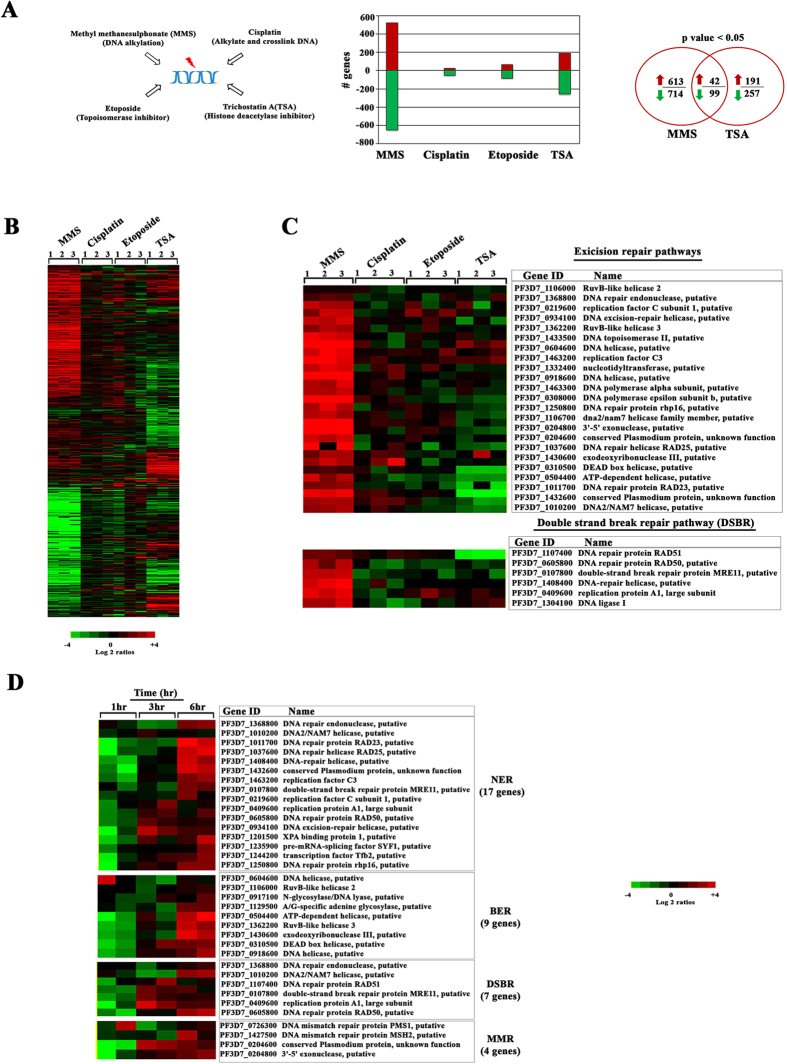
Figure 1. Global transcriptional response of P. falciparum to DNA damaging agents.
(A) Four DNA and/or chromatin perturbation agents MMS (0.05%), Cisplatin (100 μM), Etoposide (100 μM), and TSA (50 μM) were chosen to study the DNA damage response of P. falciparum parasites. The bar graph represents the number of genes differentially induced by >2 fold after synchronized parasites were treated at the trophozoite stage for 6 hr. The Venn diagram represents differentially expressed genes between the MMS or TSA treatments. (B) Heat map represents up (red) and down (green) regulated genes induced by the drug treatments by >2-fold. The results are mean value of a relative mRNA abundance in three experimental replicates. (C) The expression pattern of 29 excision and 6 DSB repair genes which were up-regulated by MMS are shown along with the effect of cisplatin, etoposide and TSA among three independent replicates (p-value < 0.05). (D) The heat map represents differential expression of DNA repair genes in a time course experiment with samples collected at 1, 3 and 6 hr of the MMS (0.05%) treatment. Only with the 6 hr of exposure to MMS, DNA repair machinery was up-regulated with 9 BER, 17 NER, 4 MMR and 7 DBSR genes significantly up-regulated in the two independent replicates (p- value 0.0002–0.02).