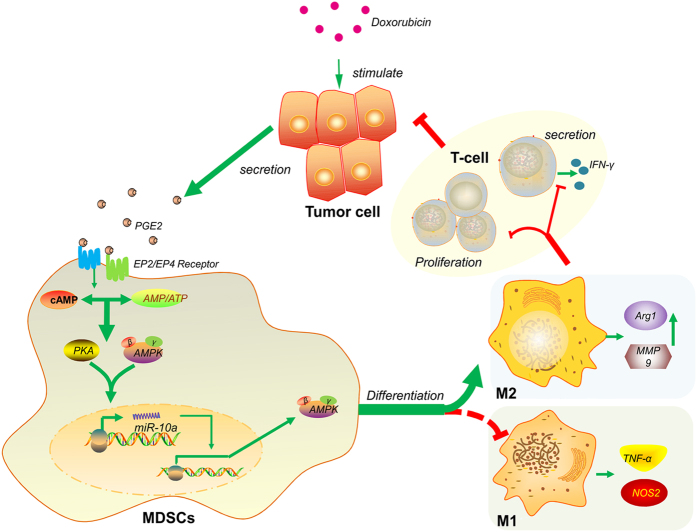
Figure 6. A schematic summary of the findings in this study to demonstrate doxorubicin induced defect of anti-tumor immunity.
Doxorubicin treatment leads to PGE2 release from cancer cells. PGE2 can target its receptors, EP2/EP4 receptors, on the surface of MDSCs to activate PKA and AMPK signaling, induce production of miR-10a and enhance AMPK signaling in MDSCs. This signaling cascade turns on expansion and polarization of MDSCs for their inhibitory action on T cells, which are responsible for anti-cancer immunity.