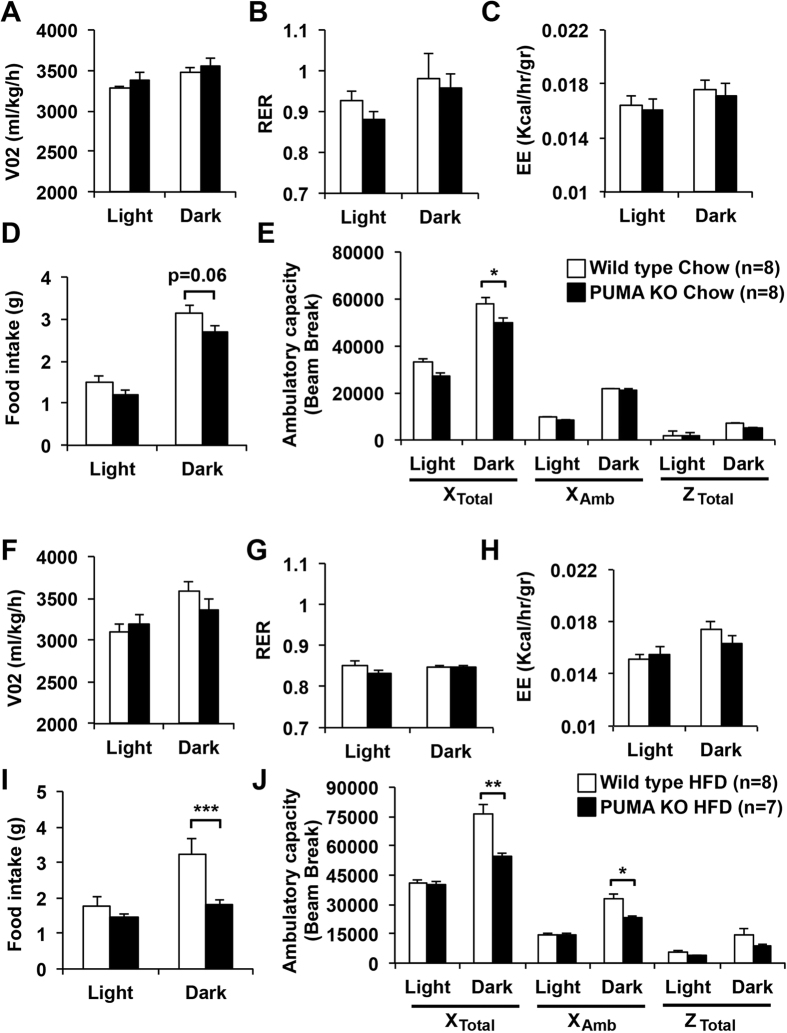
Figure 3. PUMA deficiency decreases food intake and ambulatory capacity in high fat fed mice.
Ten-week-old male wild type and PUMA knockout mice were fed a chow (A–E) or high fat diet (F–J) for 14–15 weeks. Oxygen consumption (VO2; A,F), respiratory exchange ratios (RER = VO2/VCO2; B,G), energy expenditure (C,H), daily food intake (D,I) and ambulatory activity (E,J) were assessed during the light and dark cycles for 2 consecutive days. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.