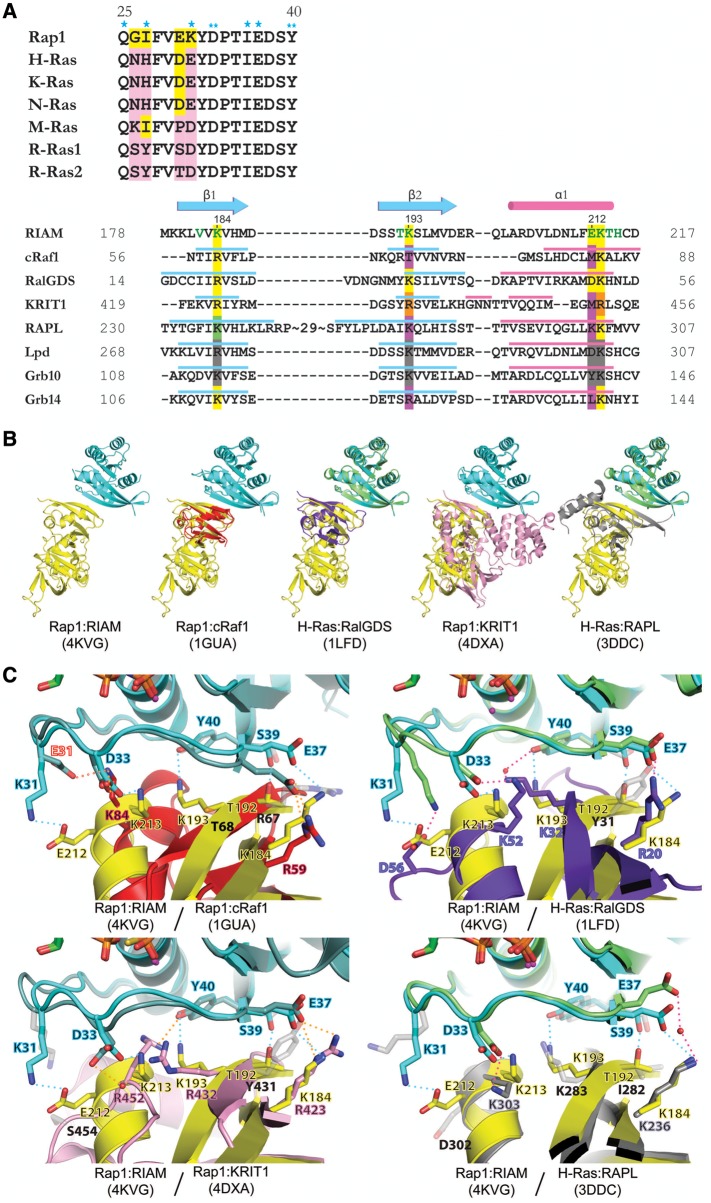
Figure 2.
Sequence and structural comparison of Rap1:RIAM and other Ras:effector complexes. (A) Structure-based sequence alignment of Switch I region of Ras family (upper panel) and Ras-binding domains (lower panel). Conserved residues are colored in yellow and non-conserved residues are colored in pink. Single asterisks indicate RIAM-interacting residues only seen in copy 1; double-asterisks denote RIAM-interacting residues seen in both copies. Secondary structure elements of the RA/RBD domain are shown in cyan (β-strand) and pink (α-helix). Green letters in the RIAM sequence indicate Rap1-interacting residues. Conserved Ras-interacting residues are highlighted in yellow. The RAPL residue highlighted in green indicates a water-mediated interaction with Ras. Non-conserved Ras-interacting residues are highlighted in purple. Arg432 and Arg452 of KRIT1 (highlighted in orange) interact with Rap1 Asp33 and Tyr40 reversely with respect to their sequence alignment. Conserved residues in Lpd and Grb10 are highlighted in gray, as no complex structure is available for comparison. (B) Superposition of Rap1:RIAM with Rap1:cRaf1 (PDB ID 1GUA, cRaf1 in red), H-Ras:RalGDS (PDB ID 1LFD, H-Ras in green, RalGDS in purple), Rap1:KRIT1 (PDB ID 4DXA, KRIT1 in pink), and H-Ras:RAPL (PDB ID 3DDC, H-Ras in green, RAPL in gray). (C) Superposition of Ras/Rap1:RA/RBD complexes for Rap1 residues Lys31, Asp33, Glu37, Ser39, and Tyr40, and corresponding interacting residues. The color scheme of the Rap1/Ras and RA/RBD ribbon models are the same as in B. The interaction formed by the mutated residue in Rap1:cRaf1 (K31E and K84, respectively) is labeled with red text and red dotted line. A water molecule is shown as a red sphere and H-bonds are denoted by dotted lines of cyan (Rap1:RIAM), orange (Rap1:cRaf1/KRIT1), or pink (H-Ras:RalGDS/RAPL). Contacting residues are labeled in colored text accordingly to the color scheme of the molecules and non-contacting residues are shown in light gray stick figures with black text.