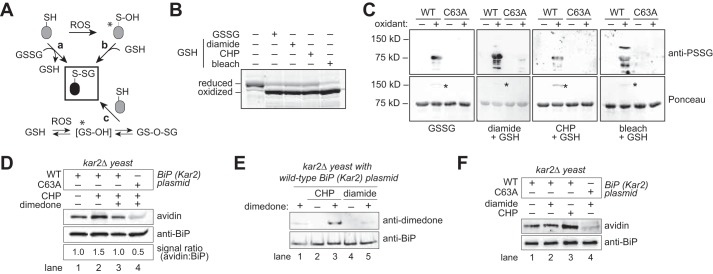
FIGURE 2.
BiP is susceptible to oxidation by reduced or oxidized glutathione. A, potential routes for protein glutathionylation (P-SSG) formation, as supported by biochemical and cellular studies (63, 64). Asterisks denote especially labile species. ROS, reactive oxygen species. B, recombinant BiP was incubated with a molar excess of oxidized glutathione (GSSG), or reduced glutathione (GSH) plus diamide, CHP, or bleach (NaOCl). Small molecules were removed by desalting, and proteins were reacted with mal-PEG5K prior to separation by SDS-PAGE and visualization with a fluorescent protein strain. Oxidized BiP denotes protein unmodified by mal-PEG5K due to the oxidation of BiP by the glutathione mixture. C, recombinant wild-type BiP or a BiP-C63A mutant was treated with oxidants as in B, separated by non-reducing SDS-PAGE, and transferred to nitrocellulose. Total BiP and glutathione-BiP adducts were detected by Ponceau S stain and anti-PSSG antibody, respectively. Note a high molecular weight band, consistent with an intermolecular BiP disulfide-bonded species, was also observed after oxidant treatment (asterisk). D, dimedone addition limits the recovery of glutathionylated BiP from peroxide-treated cells. Cells were pre-incubated with dimedone (0.1 m) for 15 min prior to the addition of 5 mm CHP. After 15 min of CHP treatment, cells were harvested, and lysates were prepared using the biotin-switch protocol. The signal ratio was set to 1.0 for cells containing wild-type BiP not exposed to any stressor. E, cells pre-treated with 0.1 m dimedone were incubated with the oxidants CHP (5 mm) or diamide (10 mm) for 15 min. BiP was enriched by immunoprecipitation; proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE, and BiP modification by dimedone was monitored using an anti-dimedone antibody. F, cell lysates from cells treated with CHP (5 mm) or diamide (10 mm) for 15 min were incubated with the dimedone-analog DAz-2. BiP was immunoprecipitated, and a Staudinger ligation reaction with phosphine-biotin was performed, allowing detection of DAz-2 with an avidin probe.