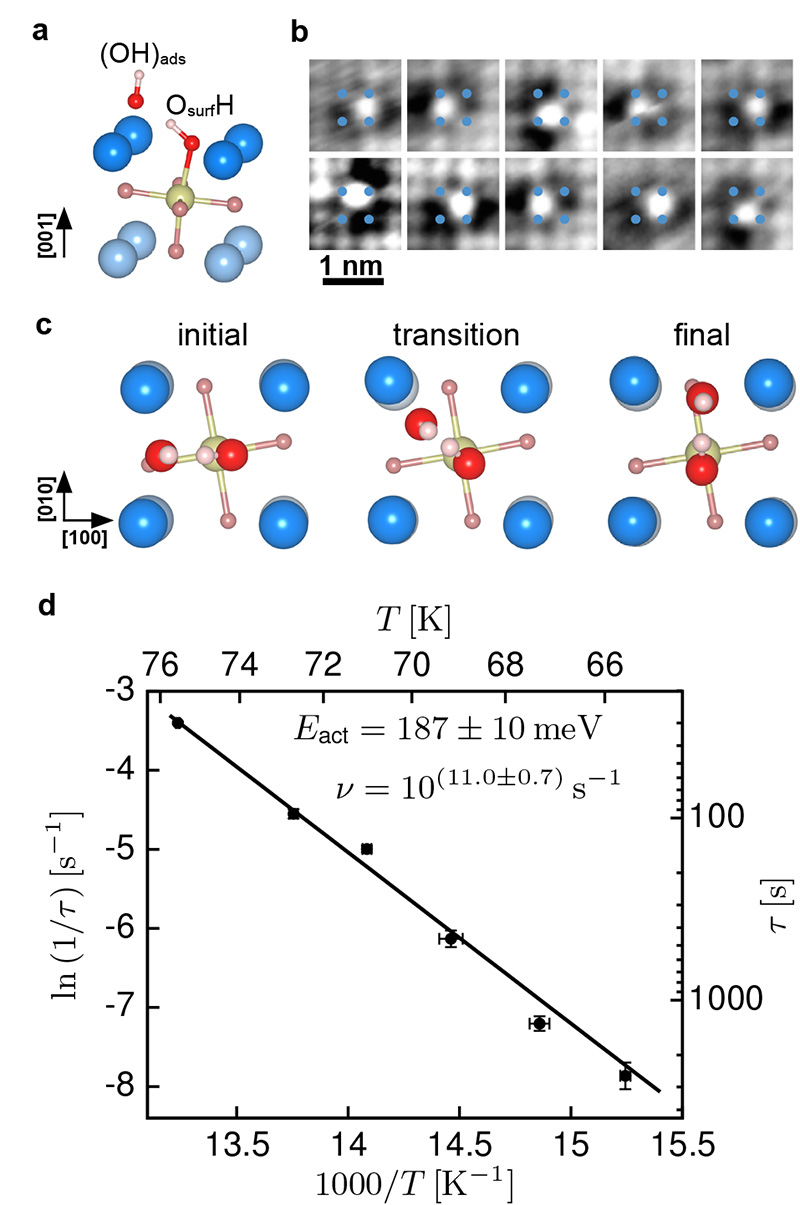
Figure 2. Dissociated water forming a ‘dynamic ion pair’.
a) Side view. Adsorption geometry of the lowest-energy configuration of a water monomer on the SrO-terminated surface of Sr3Ru2O7. The (OH)ads and the OsurfH interact through a H bond, preventing separation of the two fragments. b) A few selected, consecutive images for water monomer motion at 78 K; the (OH)ads hops between equivalent bridge sites, circling the OsurfH. c) Top view. The hopping modeled with DFT, showing the initial state, transition state, and final state; the calculations yield an activation energy of 171 meV. d) Arrhenius plot for this motion obtained from time-lapse STM movies (Supplementary Movies 1-6). An activation energy of Eact = 187 ± 10 meV and a prefactor ν = 10(11.0±0.7) s−1 is derived, see Supplementary Information.